 |
|
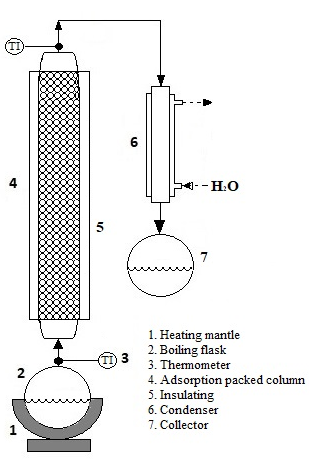
The separation of ethanol-water azeotropic mixtures by adsorption-regeneration process using a natural Mexican Clinoptilolite has been studied. For this, the equilibrium parameters were determined from experimental data obtained at the laboratory level, which were used as a starting point for the calculation of a column at Pilot Plant scale. First, on the basis of experimental data from three different sizes of natural Mexican clinoptilolite (1-2, 3 and 5 mm) and two artificial ones with 1 and 3 mm, and from the application of standard fitting techniques: Langmuir, Freundlich and linear model parameters are calculated and compared. Then, the breakthrough curves (BTC) are determined for each zeolite in a packed bed, yielding that the adsorption and capability of natural clinoptilolite is similar to those presented by artificial zeolites. The regeneration method PSA was evaluated for each zeolite. Finally, according to the experimental parameters set, a calculation of a pilot-plant scale column is included for a validation and the results are compared with the results obtained at the laboratory scale, which presented a similar behavior. We can conclude that the use of Mexican zeolite in the ethanol dehydration process could be a good low-cost alternative that is easy to apply
Keywords: Ethanol, dehydration, adsorption, pilot plant, zeolites.
|
|
 |

