 |
|
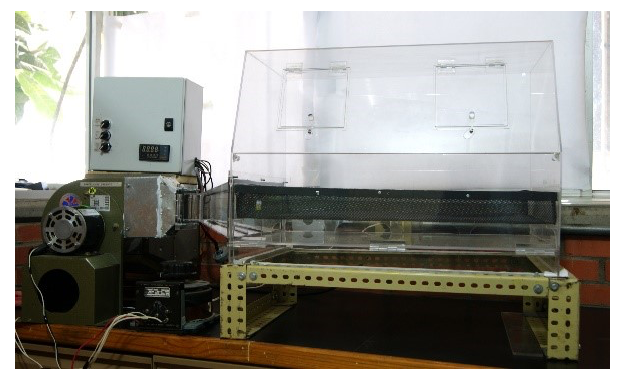
Cincho cheese is a semi-hard cheese rich in protein, with an intense flavor, slightly acidic, lumpy, soft, and firm texture, white or yellowish-white in color. Fresh cincho cheese is a highly perishable product because it doesn't have an additional conservation technique and is exposed to environmental conditions. This work aimed to study how artisanal cheese's physical, microbiological, and thermophysical properties were affected by the drying process at different temperatures. The cincho artisanal cheese was dehydrated in a prototype forced convection dryer at drying temperature (50 °C, 55 °C, and 60 °C), air velocity (0 m/s, 0.5 m/s, and 1 m/s), and particle size (0.5 mm, 25 mm, and 50 mm). The final moisture content and water activity values of dried cheese ranged from 2.74 % to 4.67 % and from 0.23 to 0.43, respectively. The microbiological analysis of the raw sample showed the presence of total coliform microorganisms (5.15 log CFU), molds and yeasts (4.99 log CFU), and lactobacillus (7.17 log CFU). The initial sodium chloride content, fat, ash, and protein content were 2.66 %, 2.75 %, 5.94 %, and 19.14 %, respectively. An increment in the sodium chloride, fat, and protein content was observed at the end of the drying process; the increment in these properties ranged from 3.8% to 6.21%, from 40.75 % to 53.90 %, and from 32.16% to 47.11 %, respectively. These properties can be combined with other foods providing the characteristics of fresh cheese.
Keywords: Cincho cheese drying, physicochemical properties, lactobacillus, convective drying, thermophysical properties, artisanal cheese.
|
|
 |

