Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 21, No. 1 (2022), Bio2699
Purification and characterization of a novel pullulanase enzyme from Bacillus thuringiensis for detergent industry
|
A. Zafar, S. Yousaf, M.N. Aftab, A. Hamid, J.I. Wattoo, A. Masood, H. Mubeen
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/Bio2699
Abstract
 |
|
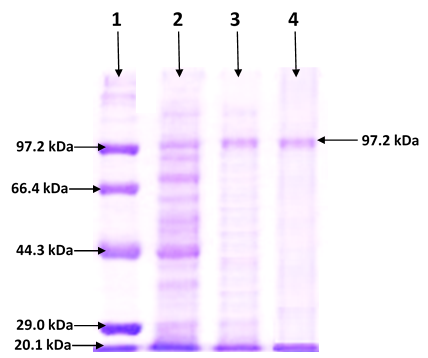
In the present study purification and characterization of a novel extracellular pullulanase enzyme from Bacillus thuringiensis was carried out for use in detergents. Maximum production of pullulanase (5.71 U/mL) was obtained in the medium containing tryptone as carbon and energy sources. The pH of media was 6.0 when it was inoculated with 3% overnight grown inoculum and incubated at 37°C for 24 h. Optimal conditions for pullulanase enzyme activity were also determined and maximum activity of enzyme (8.584 U/mL) was found with 4% pullulan as a substrate in phosphate buffer of pH 7.0 at 50°C after 20 min of incubation. Purification of pullulanase enzyme was achieved to homogeneity by ammonium sulphate precipitation as well as by ion exchange chromatography and a distinct band of 97 kDa was analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Purification fold of purified enzyme was calculated as 16.83 with 37% yield and 45.45 U/mg specific activity. The enzyme was stable up to 90°C and pH 4.0-8.0. In the presence of Ca2+ ions, the activity of the enzyme was increased, whereas EDTA found to reduce the pullulanase enzyme activity. The addition of 1% Tween 80 and Tween 20 did not show considerable effects but SDS and DMSO slow down the pullulanase enzyme activity. No significant effect of organic solvents (ethanol, methanol, acetone, isopropanol, and n-butanol) was detected on enzyme's residual activity. Purified pullulanase enzyme showed great stability with laundry detergents and wash performance was increased in the presence of pullulanase along with amylase against starchy stain.
Keywords: Pullulanase; B. thuringensis; Purification, Characterization; Detergent industry.
|
|
 |

