 |
|
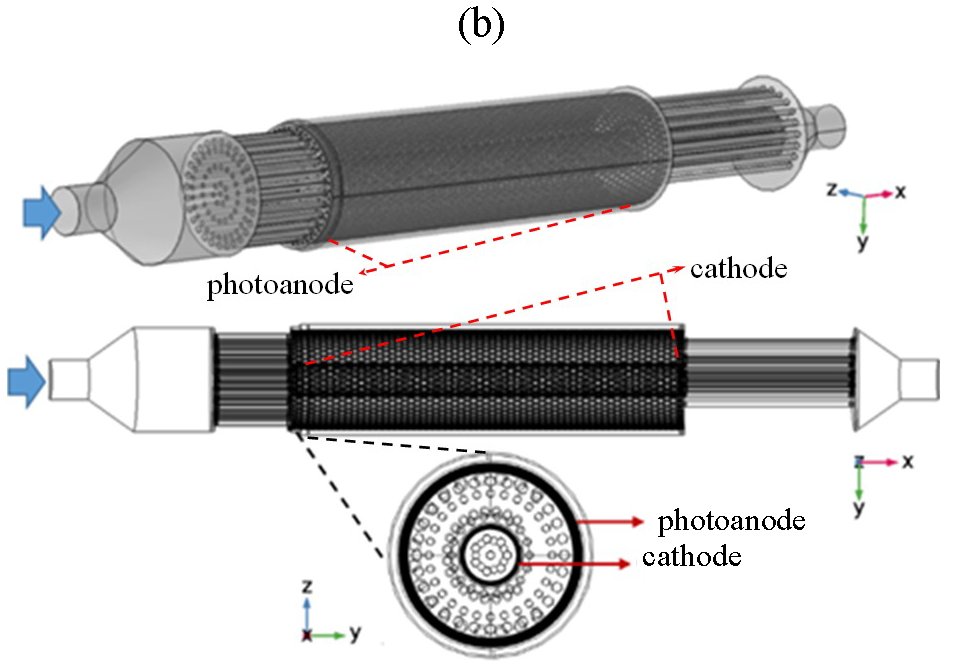
In the present work, the liquid flow pattern in a Tubular Electrochemical Reactor (TC-ECR) with concentric cylindrical expanded meshes as electrodes and inlet/outlet distributors of shower sprinkler type was evaluated. It was found that the CFD theoretical results describe the experimental F(t)-curves obtained with the methodology of “step-signal input”. Later, the F(t)-curves estimated with CFD for each reactor zone were adequately approximated with global parametric models for the development of the TER design equations. The Stagnant Zone Model with mass exchange with the anodic zone turns out to be adequate for the reactor shell zone. However, for the cathode and anode meshes, the Axial Dispersion Model with mass exchange between them proves to be appropriate. For all liquid flow rates (0.37 to 4.0 L min-1, the dispersion numbers (Nd) are in a magnitude order of small dispersion (Dax/uint Lz ≈ 0.01). This confirms that the incorporation of inlet/outlet distributors in a T-ECR improve considerably the liquid flow pattern behaviour. This experimental methodology, coupled with micro/macromixing theoretical analysis of RTD curves with CFD, can be a good alternative for the reactor design.
Keywords: Tubular Electrochemical Reactor, Cylindrical expanded meshes as electrodes, RTD by Computational Fluid Dynamic, RTD by the step-signal, Micromixing and Macromixing analysis.
|
|
 |

