 |
|
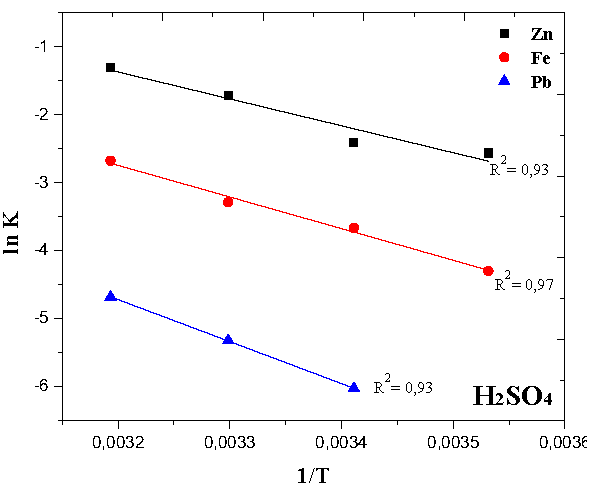
The electric Arc Furnace Dust (EAFD) sample leaching using two different organic carboxylic anions has been previously studied, as a separate article. The aim of the present research work (Part II) is the study on the leaching kinetics of EAFD, comparing the efficiency of sodium citrate with that of sulfuric acid solutions. The effect of the solid / liquid ratio, temperature and reagent concentration in the leaching solutions on the metallic dissolution was analyzed. In both cases, the more stable phase of franklinite (ZnFe2O4) experienced minimal decomposition at room temperature, although almost complete extraction of zinc was possible with sulfuric acid at higher temperatures. The kinetics of franklinite decomposition conformed to the reaction-controlled Shrinking Core Model. Using the Arrhenius expression, the apparent activation energies for franklinite and lead dissolutions in H2SO4 were evaluated. On the other hand, citrate showed promise due to its selectivity in leaching non-ferrous metals oxides (ZnO and PbO).
Keywords: Kinetics; leaching; EAFD; zinc; lead; Sodium-citrate; sulfuric-acid.
|
|
 |

