 |
|
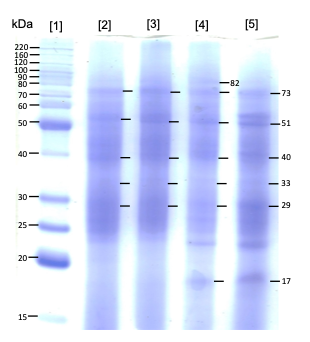
Pot experiments were conducted in a greenhouse of the National Technological of Mexico in Celaya during two summer seasons, in 2019 and 2020, to study the changes in the concentration of nutraceutical compounds and protein expression patterns in jalapeño chili pepper in response to two phytohormones (gibberellic acid and auxins) and two drying processes (lyophilization and drying by convection oven). Jalapeño chili pepper (Capsicum annuum L.) plants were treated with the phytohormones separately (gibberellic acid, 5 μM solution and auxins (2 mL/L solution)) and mixed together. The obtained results indicated that the freeze-drying process significantly preserved the concentration of nutraceutical compounds and antioxidant activity. The individual application of phytohormones led to significant increases in the concentrations of all nutraceutical compounds and antioxidant activity in the jalapeño chili peppers. The application of exogenous giberellins modified the proteins expression. An antagonist effect of the phytohormone mixture on jalapeño chili pepper production was observed, and for this reason, no jalapeño chili pepper samples were obtained. In conclusion, drying and phytohormonal treatment influence the preservation of nutraceutical compounds and antioxidant activity.
Keywords: jalapeño chili pepper, carotenoids, nutraceutical compounds, gibberellic acid, auxins.
|
|
 |

