 |
|
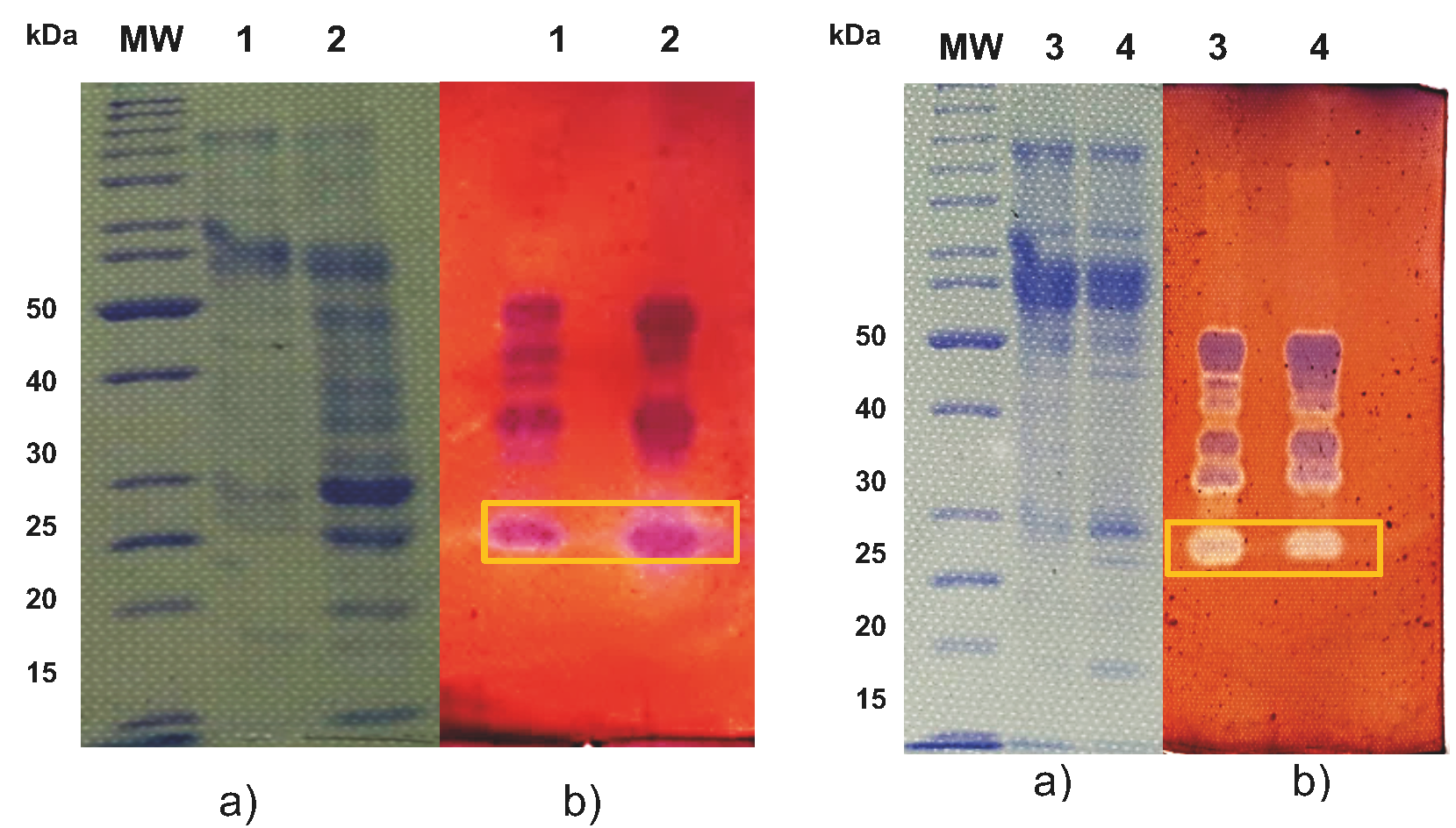
Cellulases are enzymes used in the hydrolysis of lignocellulosic residues for second-generation (2G) bioethanol production. However, the low availability in the market, and the high-cost impact in the 40 % of the total cost of 2G bioethanol production. Therefore, it is necessary to look for sustainable alternatives for its production. Cellulases are mainly produced by Aspergillus niger, and their activity can be affected by nitrogen concentration, the use of surfactants, and the carbon source. The objective of this work was to identify enzymes with CMCase (Cellulase activity of the crude extracts quantified using as substrate carboxymethyl cellulose: CMC) and β-glucosidase activity of A. niger ITV-02 from low-cost lignocellulosic residues such as corn and cob stover in two culture media (M1 and M2). The results showed that using corn stover and medium M2 increased the volumetric activity 1.4 and 1.7 times, respectively compared to corn cob and medium M2. Likewise, enzymes with cellulase activity were identified using carboxymethyl cellulose (CMC) and 4- methyl-lumberyl-β-D-glucopyranoside (MUG). The enzymes identified in MUG correspond to a glucoamylase, two β-glucosidases, and an Exo-β-xylosidase. In CMC the following were identified: Exo-β-1,3-glucanase, Endo-β-1,4 xylanase, Arabinosidase, and Endoglucanase. Corn stover does not showed a difference on CMCase and FPUase activity (cellulase activity of the crude extracts quantified using as substrate filter paper: FP) comparted to corn cob. However, improved β-glucosidase activity, suggesting that corn stover is a good raw material to produce cellulases.
Keywords: Cellulase, A. niger, glucoamylase, enzyme activity, fungi.
|
|
 |

