 |
|
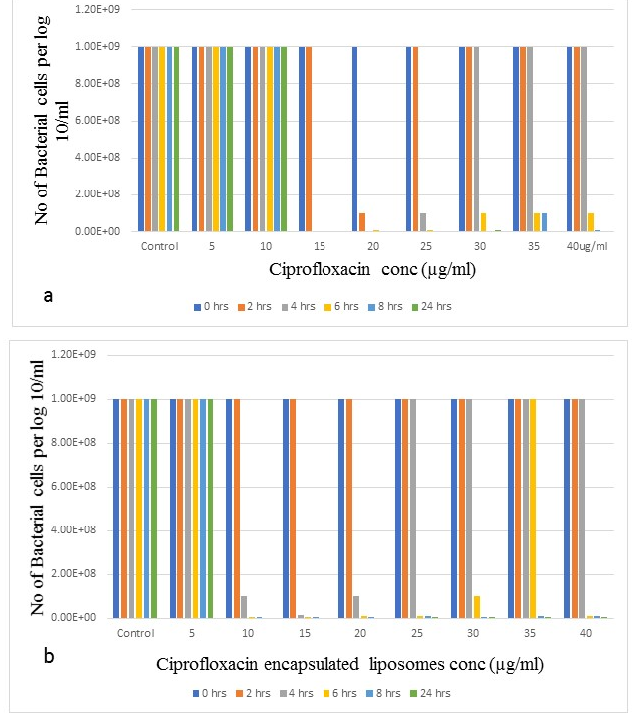
Since decades antibiotics have been used to combat diversified bacterial infections. They have also been used for a variety of other medicinal applications too. They have been a blessing to human beings in the battle against microbes, saving millions of lives. Globally, the infections caused by multidrug-resistant (MDR) bacteria are on the rise as they are gaining resistance towards antibiotics. Salmonella typhi is one such pathogen responsible for typhoid fever. It is on its way to become resistant towards antibiotics. Thus, there is a need to combat this infectious pathogen. Different nanocarriers have been used for this purpose and liposomes are well-established systems due to their high biocompatibility, bioavailability and possibility to vehiculate drugs. They are designed to carry drug safely to the action site. Currently liposomal formulations were designed to encapsulate ciprofloxacin and to analyze its in vitro efficacy against MDR Salmonella typhi. Formulations were prepared with Bx-DSPE-PEG2000 (0.1%), 100mg lipids: Phosphatidylcholine (PC) and Cholesterol (CH) at ratio of 5:3 which resulted in 93.95% encapsulation efficiency. Ciprofloxacin encapsulated liposomes reflected a faster release than usual with stability gradually reduced from 93.95% to 71.9% over the period of 9 months, with 0.7 Polydispersity index, 95.27nm particle size and -20.58mV zeta potential. Minimum Bactericidal concentration (MBC) and minimum inhibitory concentration was at lower drug concentrations i.e., 15 µg/ml, and 10 µg/ml, respectively. Conclusively, the prepared liposomes proved an effective in vitro drug delivery method against MDR Salmonella typhi.
Keywords: Salmonella typhi, Nanocarriers, Liposomes, Ciprofloxacin, Multidrug-resistant (MDR).
|
|
 |

