 |
|
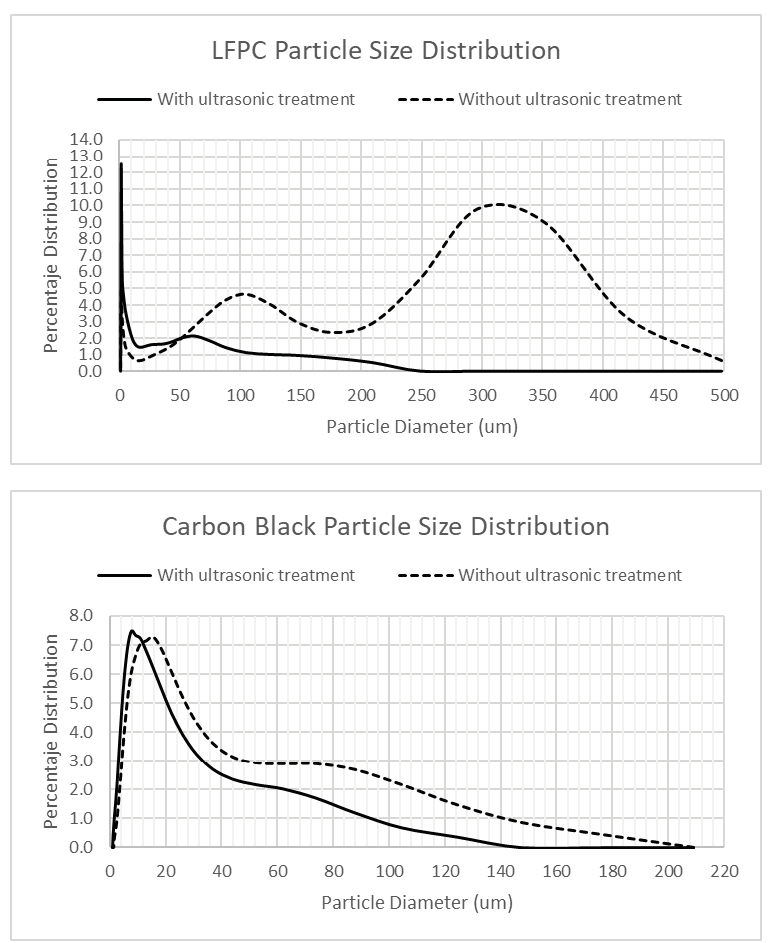
LiFePO4 has structural and electrochemical advantages that make it an important candidate as a cathodic material due to its low cost, structural stability and low toxicity. These features make it a good option for energy backup systems. However, it is necessary to address the problem of low capability to operate at high cycling speeds due to low electrical conductivity and a low diffusion coefficient. In this work, LiFePO4 powders were treated with ultrasound for different periods of time to study the effect of reducing agglomerated particles in wet mixture during manufacturing stage. Samples were characterized by a scanning electron microscope, particle-size analysis and electrochemical methods. Results revealed that ultrasonic treatment reduced particle size of both active material and conductive additive improving overall electrochemical behavior and specific capacity of samples treated for longer periods of time.
Keywords: LiFePO4, Battery, Cathode, Particle size.
|
|
 |

