 |
|
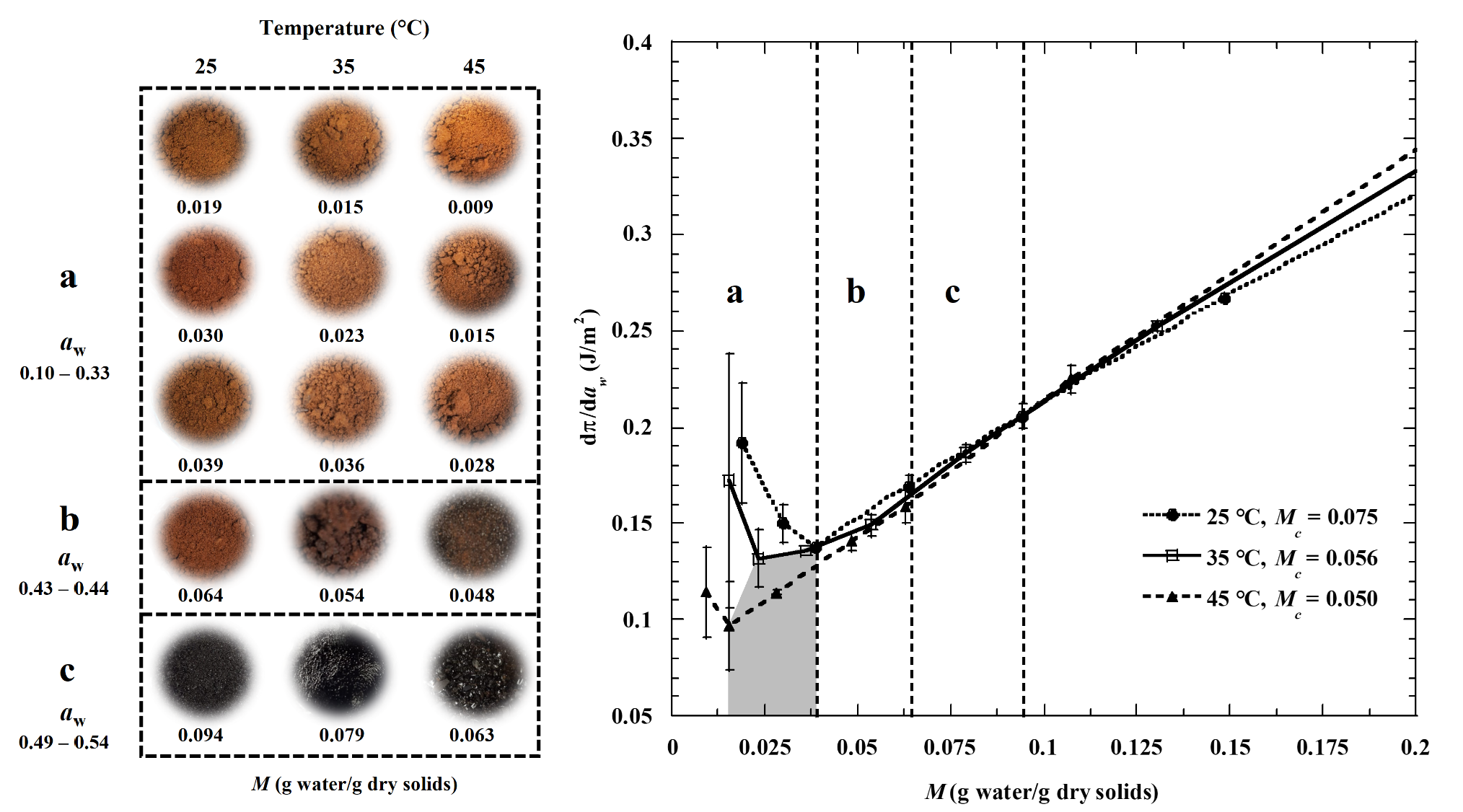
In this work, the values of monolayer (Mo) of the GAB model, generalized GAB model, and minimum change in spreading pressure (MCSP) of the adsorbed water were compared to determine the optimal storage conditions of spray-dried coffee powder. The effect of the adsorption models on estimating the water-vapor permeance of the packaging material and the product’s shelf-life was also evaluated. For this, the powder was packed in a plastic film and stored at three temperatures and two relative humidities (RH). As a result, the best physicochemical stability of the powder was achieved at water contents corresponding to MCSP, from 0.01-0.04 g water/g dry solids. It was also observed that the most extended shelf-life was 246 days, obtained at 25 °C/75 HR with a permeance of 1.45 x 10-4 g/m2dPa, and the shortest was 8 days at 45 °C/97 HR with a permeance of 4.2 x 10-4 g/m2dPa. Additionally, it was determined that the degradation rate tripled (Q10 ≈ 3) every 10 °C with activation energies greater than 90 kJ/mol. The results show that the spreading pressure contributes to ensure the quality of water-soluble foods.
Keywords: Spreading pressure, Shelf-life, Water-vapor permeance, Monolayer, Adsorption model.
|
|
 |

