 |
|
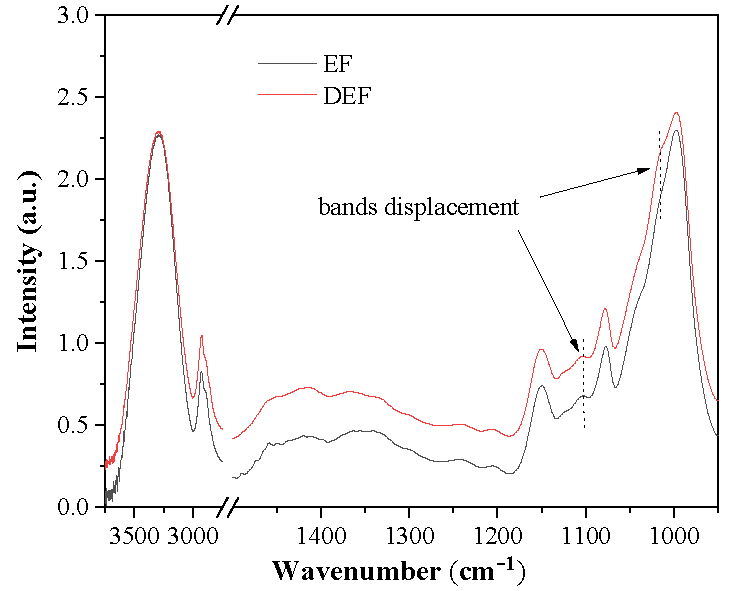
This study aimed to evaluate the effect of SiO2 nanoparticles on the mechanical, structural, and physicochemical properties of sweet potato (Ipomoea batatas) starch edible films. Two edible films were made, films without SiO2 nanoparticles (EF), and films with SiO2 nanoparticles (DEF). The tensile strength for EF and DEF was 23.79 MPa and 24.65 MPa, respectively, and the elasticity for EF and DEF was 1.53% and 1.13%, respectively. The water vapor permeability, solubility, and water absorption for EF were 2.2 x 10-9 g/m·s·Pa, 19.52% and 4.51%, while for DEF they were 1.7 x 10-9 g/m·s·Pa, 18.19%, and 3.03%, respectively. According to FTIR results, the SiO2 nanoparticles increased the short-range crystallinity of starch and reduced water vapor permeability without affect its mechanical properties.
Keywords: solubility, permeability, elasticity, tensile strength, crystallinity.
|
|
 |

