 |
|
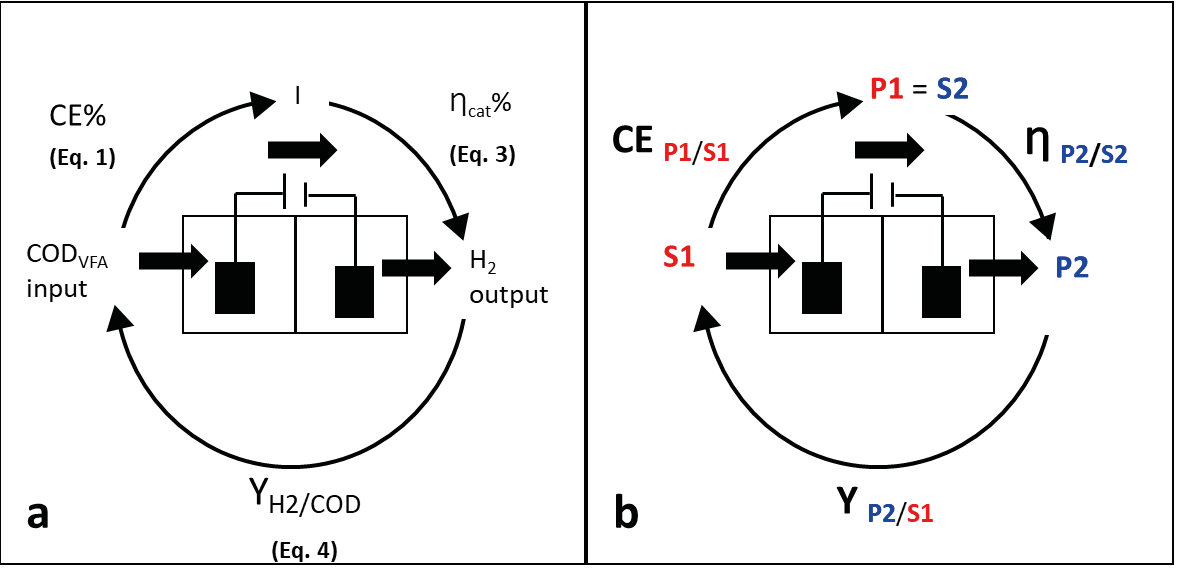
Microbial electrolysis cells (MECs) are hybrid systems that include characteristics of bioreactors and electrochemical cells. Primary parameters, such as substrate removal, current density and hydrogen production, and secondary parameters, such as coulombic efficiency, cathodic efficiency and hydrogen yield, determine the performance of MECs. The present work aimed to assess primary and secondary parameters in an MEC fed volatile fatty acids (VFAs) to determine those that most reliably describe the MEC performance in a model setup for hydrogen production. MECs were operated at 0.6 V and fed acetic, propionic and butyric acid mixtures in successive feeding cycles. The main performance parameters were chemical oxygen demand removal COD (84.7 ± 0.5 %), current density (378 ± 7 mA m-2) and hydrogen production (267 mL L-1 d-1), which resulted in repeatable and more reliable efficiency parameters when MECs were fed acetate than when they were fed VFA mixtures. Both the current density and hydrogen production curves showed similar inflection points, thus giving accuracy to the cathodic efficiency determination (162.1 % -169.6 %). Hydrogen yield was not a reliable parameter with the three-VFA mixture since hydrogen production and COD removal curves showed no correlation. These findings indicate that MEC assessment should be verified via the correspondence between primary and secondary parameters.
Keywords: cathodic efficiency, coulombic efficiency, hydrogen yield, MEC, reliability.
|
|
 |

