 |
|
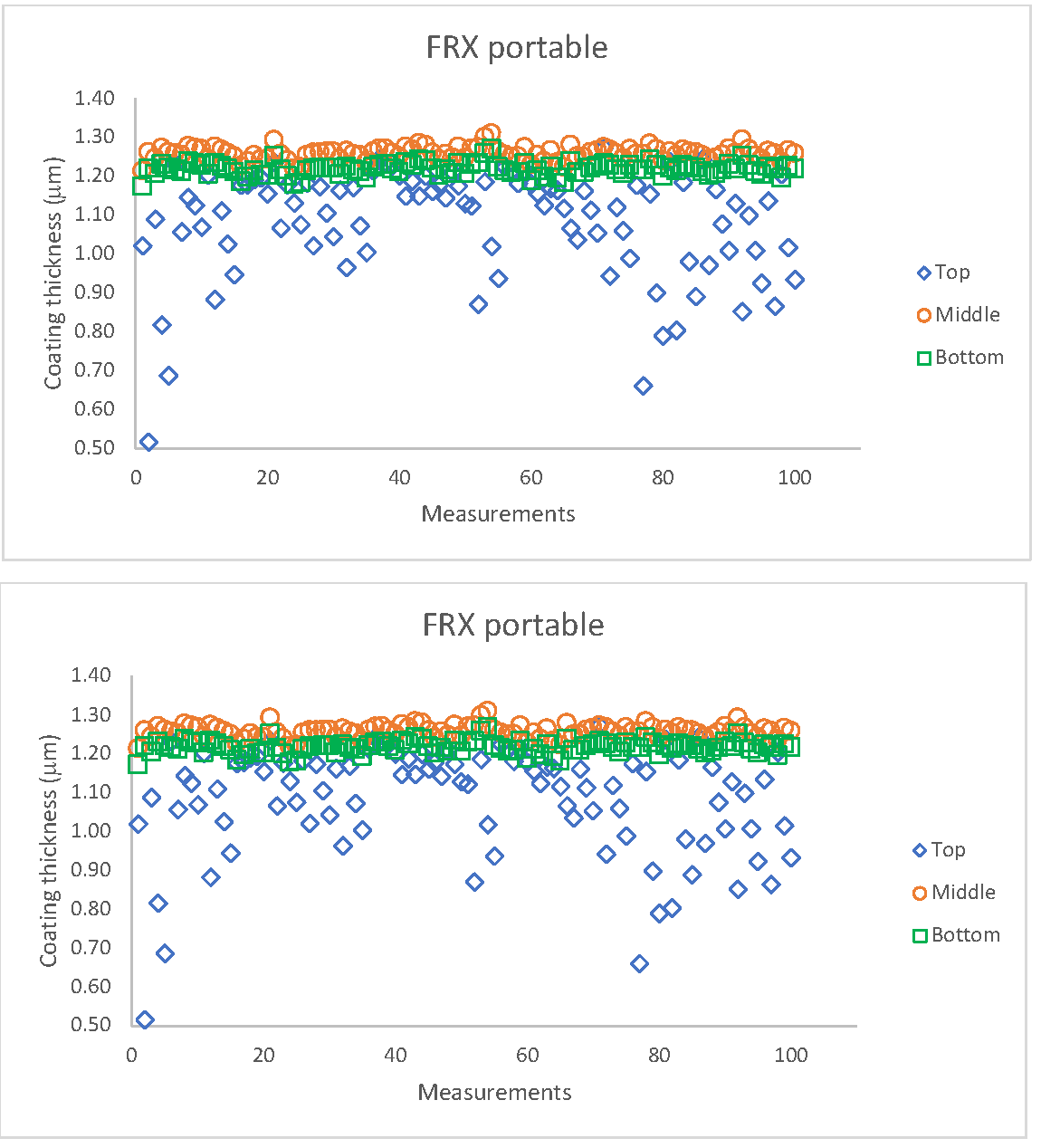
The purpose of this research is to develop reference Ti-coatings and analyze the thicknesses evaluated via destructive (DT) and non-destructive (NDT) measurement techniques. The Ti coating was deposited on a mirror finished AISI M2 steel by the magnetron process. The nominal value of the coating thickness was 1 μm. The NDT was the X-Ray Fluorescence (XRF) method, the thickness for the portable analyzer was 1.18 ± 0.19 μm and the thickness using the spectrometer XRF was 1.17 ± 0.24 μm. For DT, thickness measurements were carried out in the cross-sections of the Ti-coatings, using the Field Emission - Scanning Electron Microscopy equipped with Energy Dispersive Spectrometer (FE-SEM-EDS). The coating thickness measurements were performed with image analysis of secondary electrons (SE), backscattering electrons (BSC), mapping (MAP) and elemental profiles (LS) using ImageJ and Aztec software. The results of the thickness measurements are SE: 1.12 ± 0.15 μm, BSC: 1.14 ± 0.13 μm, LS: 1.25 ± 0.13 μm and MAP: 1.29 ± 0.6 μm. Variations in the results were identified and estimated in the uncertainty models proposed for each method.
Keywords: coating thickness, magnetron sputtering, titanium, destructive measurement, non-destructive measurement.
|
|
 |

