 |
|
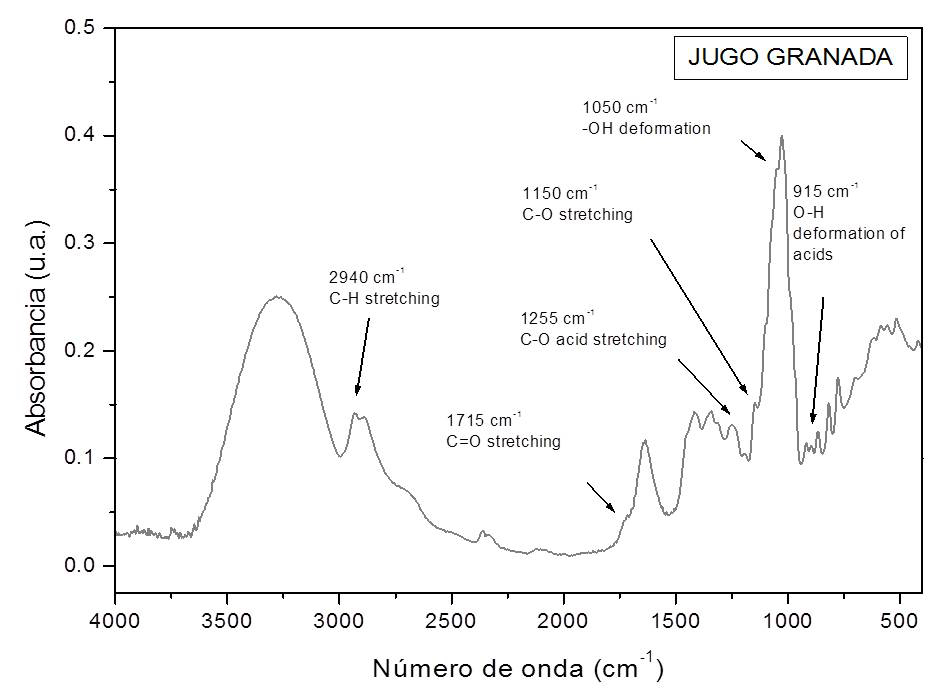
Shortwave ultraviolet radiation (UVC) has been utilized to increase the tensile strength of edible films because it induces the crosslinking process. In this study, films were elaborated with pomegranate juice and chitosan. Films were exposed to selected dosages UVC and its effect on color, mechanical properties, permeability and water solubility of edible films were determined. Additionally, studied films were analyzed by FTIR spectroscopy in order to determine possible structural changes. UVC radiation increased the tensile strength and rigidity of the studied films, but their elongation decreased. The permeability of films decreased with UVC dosage, while their water solubility was not affected. The net color change of studied films increased as UVC dosage was increased. According to FTIR analysis, UVC radiation produced structural changes in edible films, which were more important at the highest tested dosage (1555.2 J/m2).
Keywords: pomegranate juice, chitosan, edible films, FTIR, UVC radiation.
|
|
 |

