 |
|
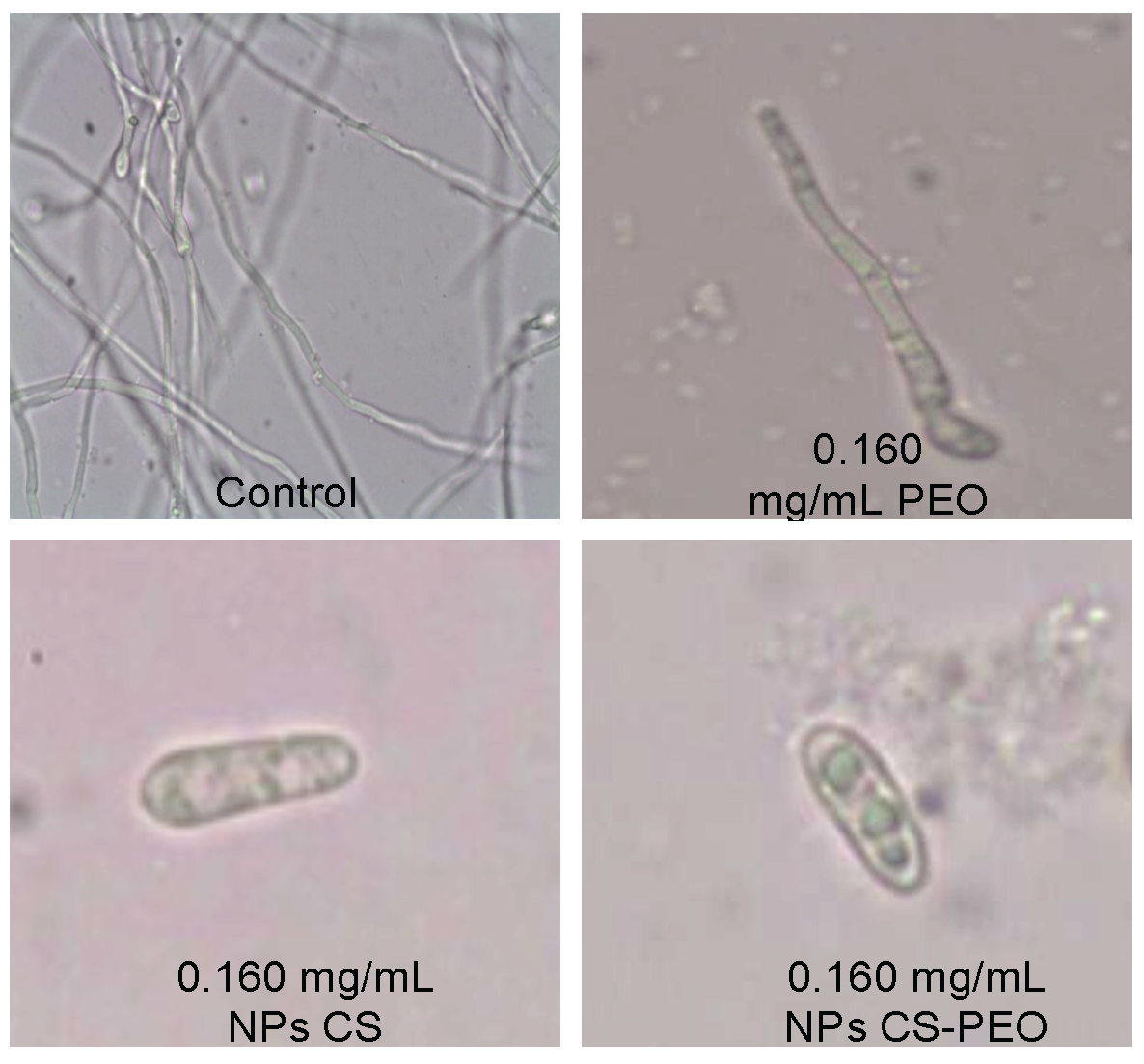
Recent studies have demonstrated that the micro and nanoparticles of chitosan (CS) have an in vitro antifungal effect against filamentous fungus that are of importance in food. This study was made to evaluate the antifungal activity of chitosan nanoparticles, pepper tree essential oil (PEO), and chitosan biocomposites loaded with pepper tree essential oil (CS-PEO), on the in vitro growth of Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. The particles were obtained by nanoprecipitation and the size and superficial charge (Z potential) were evaluated using dynamic light dispersion analysis (DLS). The mutagenic potential and the acute toxicity were also evaluated. The effect on the radial growth, spore’s germination, viability, and damage to the membrane´s integrity, were determined. The effect on the kinetic growth parameters was also determined. Results showed that the CS and CS-PEO particles diameter was 341.2 ± 12.40 and 355.3 ± 25.3 mm, respectively. In vitro assays showed both nanoparticles with a high inhibition potential on C. gloeosporioides, and low mutagenicity and toxicity. At a concentration of 0.160 mg/mL, the CS-PEO biocomposite presented a greater (P<0.05) inhibitory effect on radial growth, spore germination and viability of the spores, this constitute a natural alternative to the use of fungicidal chemical agents for fungus control.
Keywords: chitosan, Schinus molle, biocomposites, antifungal effect, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides.
|
|
 |

