 |
|
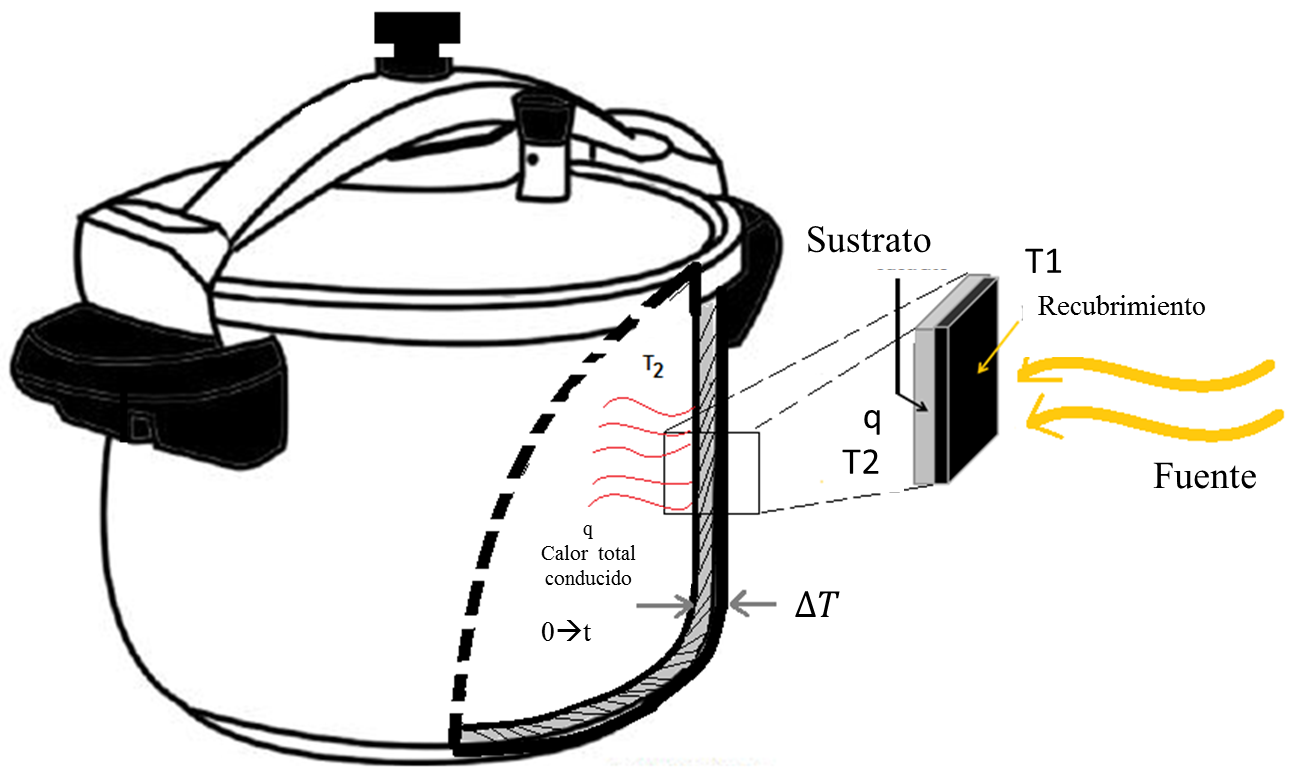
The present work shows the development of a low cost coating based on forest biomass soot, used to form solar absorbent surfaces for use in solar thermal technologies, such as solar cookers. A coating with an acrylic as a binder has been developed to be able to adhere the coating to metal surfaces. To characterize the thermal behavior of the metallic surfaces with the proposed coating, a theoretical and experimental methodology was designed. Experimentally the biomass soot coating was compared with a commercial high temperature paint used in solar thermal technologies. Through standard field tests for solar cookers, it was possible to corroborate the methodology suggested on metal surfaces with soot coatings; additionally the selectivity of the sooty surfaces was estimated, the results were similar to the thermal characterization. Finally, due to the coating's functionality, it was applied to 37 solar cooking systems that were implemented in an indigenous community in the state of Michoacán, Mexico. Due to the above, many applications of the developed coating are glimpsed.
Keywords: solar absorber, soot, thermal performance, cooking power.
|
|
 |

