 |
|
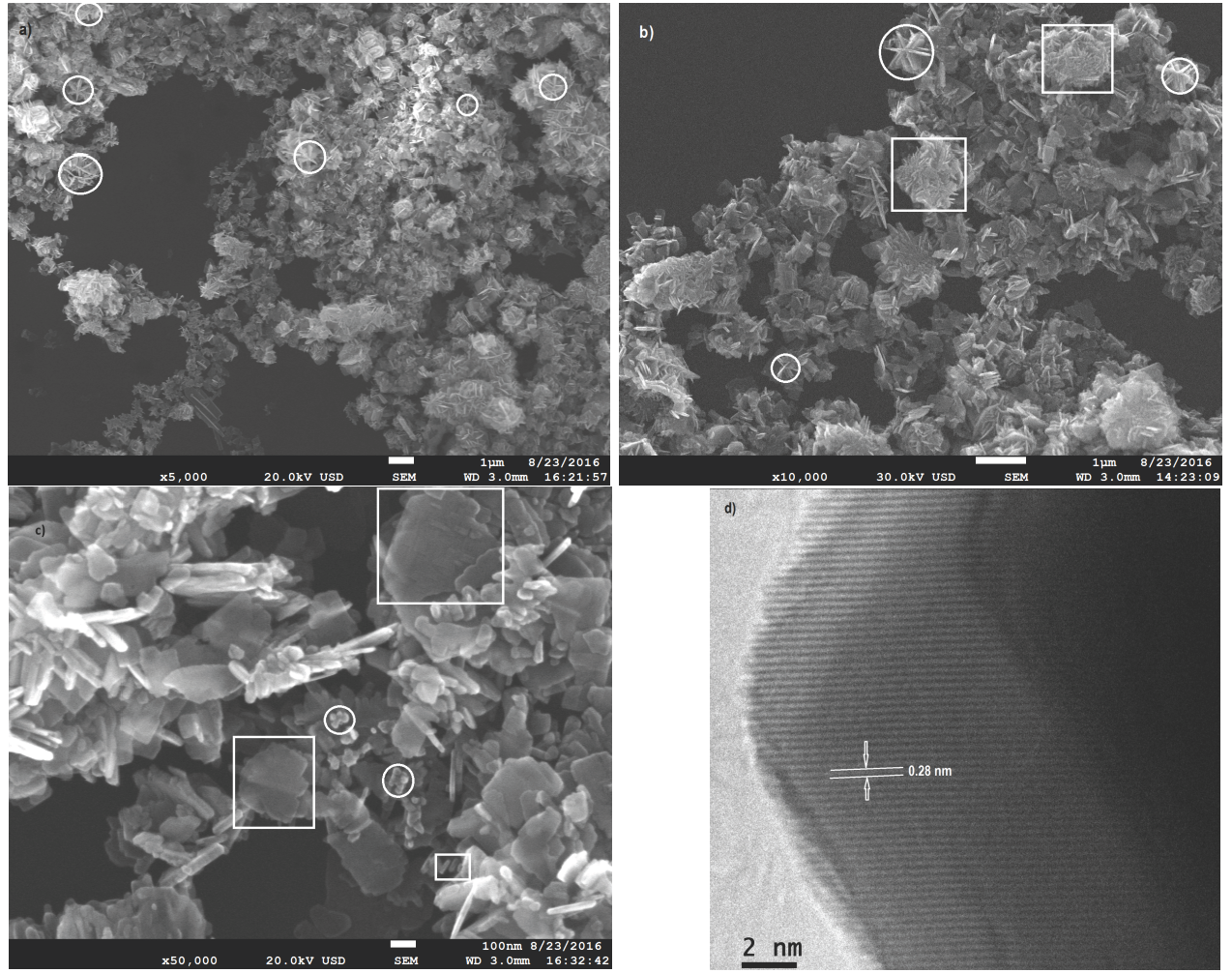
In this work a simple chemical route was employed to synthesize ZnO nanoparticles by precipitation from aqueous solution of ZnCl2 as precursor, NaOH as oxidizing and sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) as surfactant. Samples of ZnO nanoparticles were analyzed by scanning electron microscopy (SEM), FTIR spectroscopy, Raman spectroscopy, X-Ray diffraction, UV/Vis-NIR diffuse reflectance, high resolution transmission electron microscopy (HR-TEM), and N2 adsorption-desorption. It was observed from SEM analysis that ZnO nanoparticles with morphologies resembling six-blade impeller with diameters in the range of 500 nm to 1 mm, and sheet-like (approximately 200 × 300 nm) were obtained through this technique. X-Ray diffraction and Raman analyses confirmed the obtaining of hexagonal wurtzite ZnO crystal structure. The calculated band gap energy was 3.19 eV, which is slightly lower than the average value reported in the literature. Specific BET area of ZnO nanoparticles was 26.5 m2/g.
Keywords: ZnO, microstructures, band gap energy, SEM, morphology.
|
|
 |

