 |
|
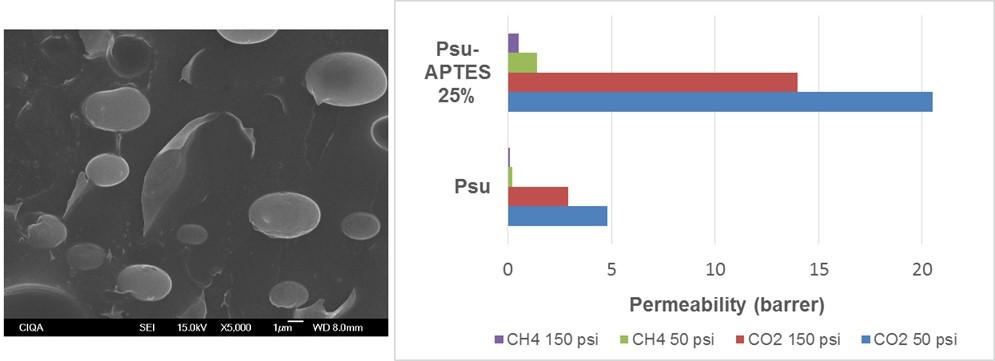
This work reports the synthesis in-situ of silica particles inside a polysulfone matrix by the sol-gel method in acidic medium using different polymerization inorganic precursors: tetraethylorthosilicate (TEOS), 3-aminopropyltriethoxysilane (APTES) and mixture of them. The effect of the type of inorganic precursor on the formation of silica particles was studied. Composite membranes were prepared by casting technique from these organic-inorganic materials. These membranes were characterized by X-ray diffraction (XRD), infrared spectroscopy (FTIR), differential scanning calorimetry (DSC) and thermogravimetric analysis (TGA). The morphology, particle size and particle-polymer interaction were studied by scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Additionally, a semi-quantitative chemical analysis by energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy (EDX) showed the chemical composition of the composite membranes. Type and concentration of silica precursor affected the morphology, particle size and distribution of silica in the composite membranes. Composite membranes with no interfacial voids were obtained from APTES at 25 wt%. Initial studies about the gas separation properties of CO2/CH4 gas mixture revealed an improvement on the CO2 permeability of composite membrane comprising silica particles synthesized from APTES in comparison with the polymeric membrane.
Keywords: silica, sol-gel, polysulfone, composite membrane, gas separation.
|
|
 |

