 |
|
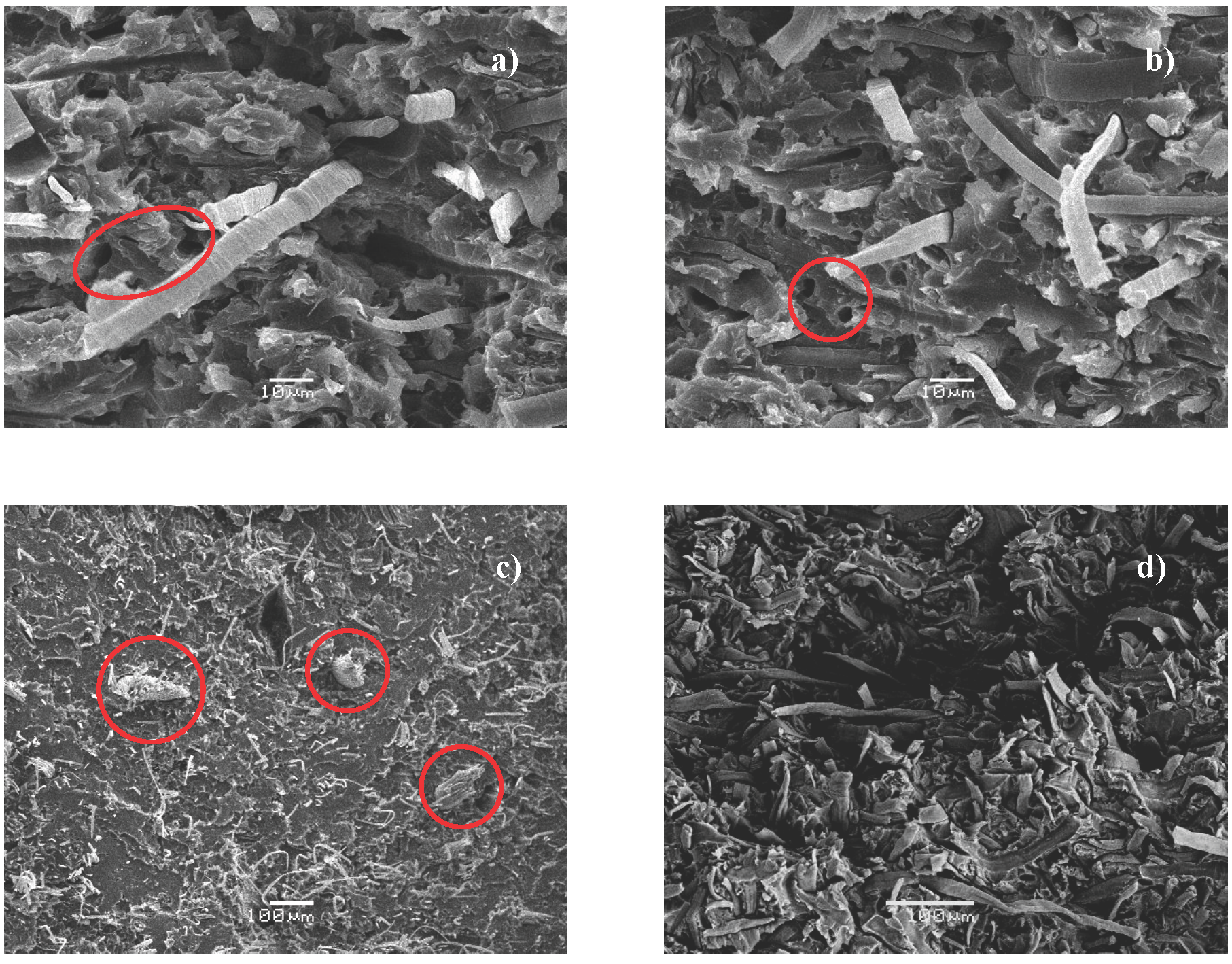
Eco-composite materials have gained the interest of academia and industry due to their environmentally friendly features. In this work, two groups of eco-composites of cellulose acetate matrix reinforced with cellulose and curauá fibers were prepared by extrusion and injection method. The first group of eco-composites, were prepared on laboratory scale, with curauá fibers, virgin and treated by two different methods; extraction with acetone and mercerized. A second group of materials was obtained on pilot scale, for which cellulose fibers and curauá fibers treated with acetone were used at different times of extraction. The acetone treatment was selected because in the first group, the materials with these fibers presented better mechanical properties, and mainly for their lower thermal conductivity (0.132 W m-1 K-1), compared to those from untreated fibers (0.178 W m-1 K-1) and treated with NaOH (0.255 W m-1 K-1). The eco-composites prepared on a pilot scale with curauá fibers previously treatment with acetone for 5 days presented a better balance of their thermal and mechanical properties, which could allow their use as thermal insulation with high mechanical performance (thermal conductivity = 0.097 W m-1 K-1 and modulus of elasticity = 2.2 GPa).
Keywords: green-composites, cellulose fibers, thermal insulating, curauá, cellulose acetate.
|
|
 |

