 |
|
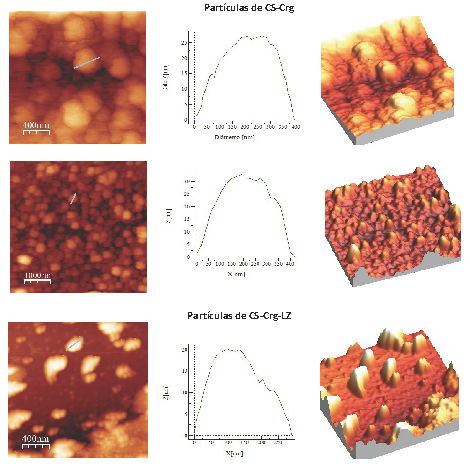
In this study, particles of chitosan-carrageenan (Cs-Crg) and chitosan-carrageenan-lysozyme (CS-Crg-LZ) were synthesized by ionic complexation. The particles were analyzed by atomic force microscopy, dynamic light scattering and FT-IR, and the percentage of association of lysozyme was determined. The biological activity of the particles was evaluated by viability assays of Aspergillus parasiticus spores and cytotoxicity in ARPE-19 cells. The effect on subcellular structures was analyzed by fluorescence microscopy. The addition of lysozyme reduced the size of the particles. The size and Z potential of the synthesized particles were 725±5.5 and 250±8.1 nm and 28.7±1.0 and 21.6±0.8 mV for CS-Crg and CS-Crg-LZ, respectively. CS-Crg-LZ and CS-Crg particles exhibited a higher (p<0.05) inhibitory effect on the viability of A. parasiticus with respect to control, which increased proportionally to the particles concentration. None of the particles showed a mutagenic effect and they did not present cytotoxicity in ARPE-19 cells; likewise, no changes were observed in cell morphology with respect to control, observing normal structures in the actin cytoskeleton and in the DNA structure. These results show that chitosan-based particles are a feasible and safe option for the control of pathogenic fungi of agricultural-food interest.
Keywords: carrageenan, biocomposites, subcellular structures, cytotoxicity, protein release.
|
|
 |

