 |
|
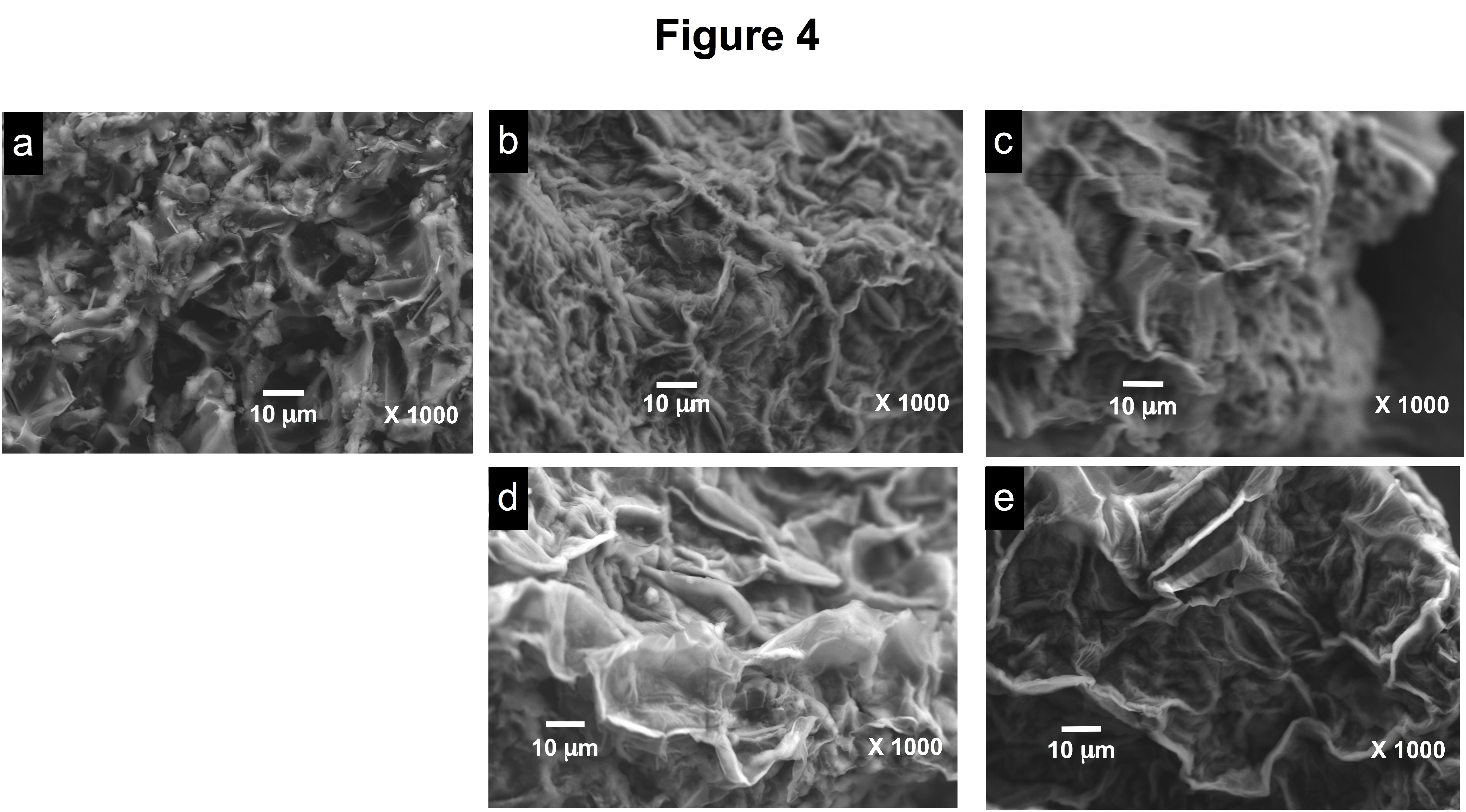
Eichhornia crassipes leaves (LEC) have been shown to be a highly effective biosorbent for the toxic dye Acid Red 27 (AR27). For continuous application, LEC biosorbent must be regenerated with a suitable desorption agent. The recovery of bound AR27 and the subsequent reuse of LEC were investigated in the present work over seven AR27 biosorption–desorption cycles. Desorption studies showed that the LEC-biosorbed dye could be effectively desorbed (100% efficiency) using dilute NaHCO3 solution (0.025 M). Moreover, the biosorbent could be used effectively for at least seven biosorption–desorption cycles without any apparent physical change or damage and with undiminished AR27 biosorption capacity. The AR27 biosorption kinetics was well described by a pseudo-second-order model, whereas a pseudo-first-order model best described the AR27 desorption kinetics. Thus, LEC exhibits remarkable potential for application in detoxification of AR27-contaminated aqueous solutions.
Keywords: acid Red 27 dye, biosorption, desorption, Eichhornia crassipes, biosorbent regeneration.
|
|
 |

