 |
|
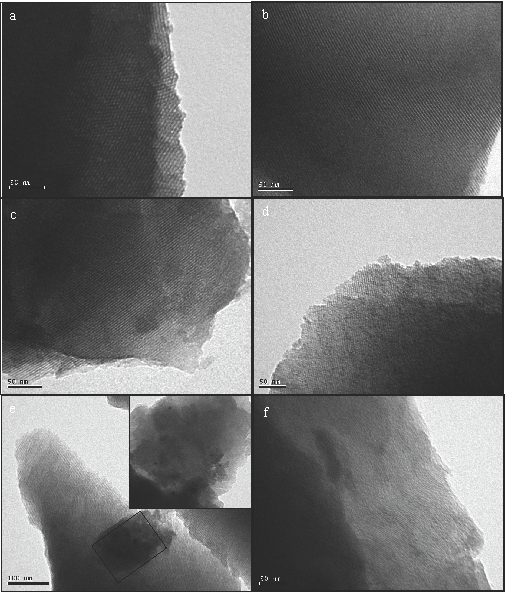
Mesoporous silica material type MCM-41 was modified with different amounts of Zn (1 - 15 wt.%) by the wet impregnation method. Support and catalysts were characterized by means of powder X-ray diffraction (XRD), N2 nitrogen adsorption–desorption, transmission electron microscopy (TEM), X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy (XPS) and ICP-OES techniques. The Zn-modified mesoporous silicates have been successfully tested for the degradation in aqueous solutions of different endocrine-disrupting (EDs), such as herbicides (atrazine), compounds derived from the plastic industry (bisphenol A) and from the pharmaceutical industry (clofibric acid). The results showed that the Zn/M(5) catalyst exhibited the highest activity. The high performance of this material indicates that the heterogeneous photo-Fenton-like reaction appears as a very promising pre-treatment capable of enhancing the biodegradability of water contaminated with biorecalcitrant chemicals, as the most endocrine disruptors.
Keywords: MCM-41, Zn, advanced oxidation process, endocrine disruptors.
|
|
 |

