 |
|
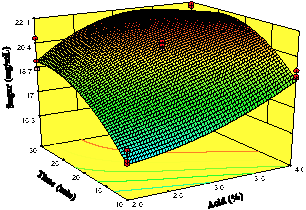
The self-sustaining nature of renewable energies makes it necessary to continuously search for substrates that satisfy a growing interest in the production of biofuels, taking care of areas such as food security. In this work we optimized a hydrolysis process of Opuntia ficus-indica cladodes using acid diluted and surface response methodology. The nopal is a secondary crop widely distributed in arid and semi-arid zones and recently investigated for its potential in the biofuel industry given its versatility as a crop. The result of this optimization was the production of 20,825 mg mL-1 of total reducing sugars (TRS), at 27.25 minutes of reaction and with a solution of 3.46 % sulfuric acid. The main sugars obtained in the hydrolyzed were galactose (57.14 %), arabinose (20.51 %), glucose (13.18 %) and xylose (9.17 %). Also, it emphasizes the value of humidity of this culture (90 %) and the low amount of lignin present (2.70 %).
Keywords: optimization, Opuntia ficus-indica, second-generation biofuels, solid-liquid relationship.
|
|
 |

