Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 17, No. 3 (2018), IA9
Microporous activation carbon made of sawdust from two forestry species for adsorption of methylene blue and heavy metals in aqueous system – case of real polluted water
|
J.F. Cruz, G.J.F. Cruz, K. Ainassaari, M.M. Gómez, J.L. Solís, R.L. Keiski
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/IA9
Abstract
 |
|
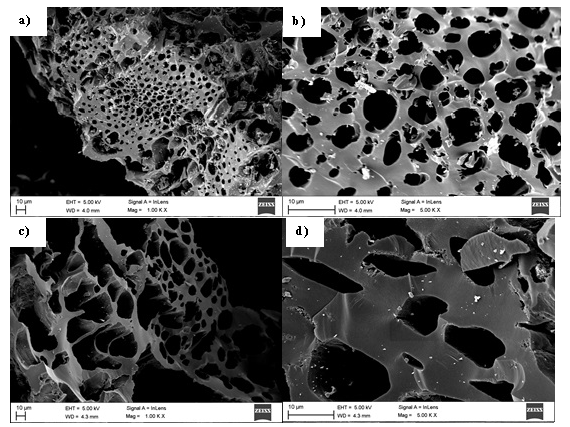
Activated carbon samples were prepared and characterized from two novel forestry precursors by one-step chemical activation with ZnCl2. The adsorption capacities of the adsorbents were tested with methylene blue in monocomponent synthetic solution and with heavy metals from polluted river water. The specific surface areas (SBET) of the produced activated carbons were 1278 and 1404 m2/g. Further characterization was carried out by FTIR, RAMAN spectroscopy, XRD and FESEM analysis. The pore structure of both activated carbons was predominantly microporous with presence of mesopores. The maximum methylene blue (MB) adsorption capacities for both activated carbons were 250 mg/g and 357 mg/g. MB kinetic experiments were carried out and the influence of the initial MB concentration and the activated carbon dosage was evaluated. The samples reached removal levels close to 100% during the first 5 min of experiments with dissolved As(V) and Pb(II) in the polluted river water, reducing the concentration of these elements until levels below the local water quality standards.
Keywords: sawdust, adsorption, methylene blue, heavy metals, aqueous system.
|
|
 |

