 |
|
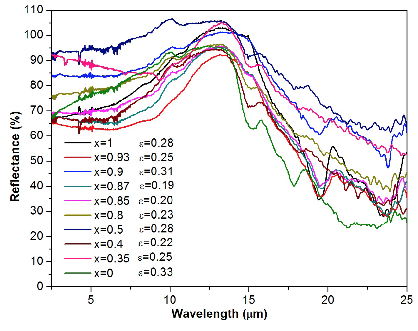
In this research new materials are proposed to improve the capacity of solar energy absorption of solar thermal devices, such as distillers and flat plate solar collectors. The synthesis of a composite series of the system (FexMn1-x)2O3 was proposed and its structural and optical properties were characterized. The crystal structure and optical properties were evaluated using X-ray diffraction and UV-Vis-IR spectroscopy techniques, respectively. To determine the relative concentration of hematite and bixbyite-type crystal phases as a function of the relative concentration of iron and manganese in the compounds, different refining analyzes were performed by the Rietveld method. X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy showed only the presence of trivalent metal species. The main results of analyzing the proposed system were: 1) the optimum manganese concentration and 2) solubility limits of Mn3+ and Fe3+ into the hematite and bixbyite structures, respective. The found values of solar absortance (αs) and thermal emission (εt) indicated that the addition of manganese is crucial for pigments performance used in solar absorption applications. The effects of the chemical composition on solar selectivity (αs/εt) are discussed.
Keywords: pigments, bixbyite, hematite, Rietveld refinement, manganese.
|
|
 |

