Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 17, No. 3 (2018), Mat87
Study of silica nanocomposites for bumper fascia: mechanical, chemical characterization and impact simulation
|
P.A. Bravo-Carrasco, M. Salazar-Hernández, E.E. Pérez-González, J.M. Mendoza-Miranda, H. Juarez-Rios, R. Miranda-Avilés, C. Salazar-Hernández
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/Mat87
Abstract
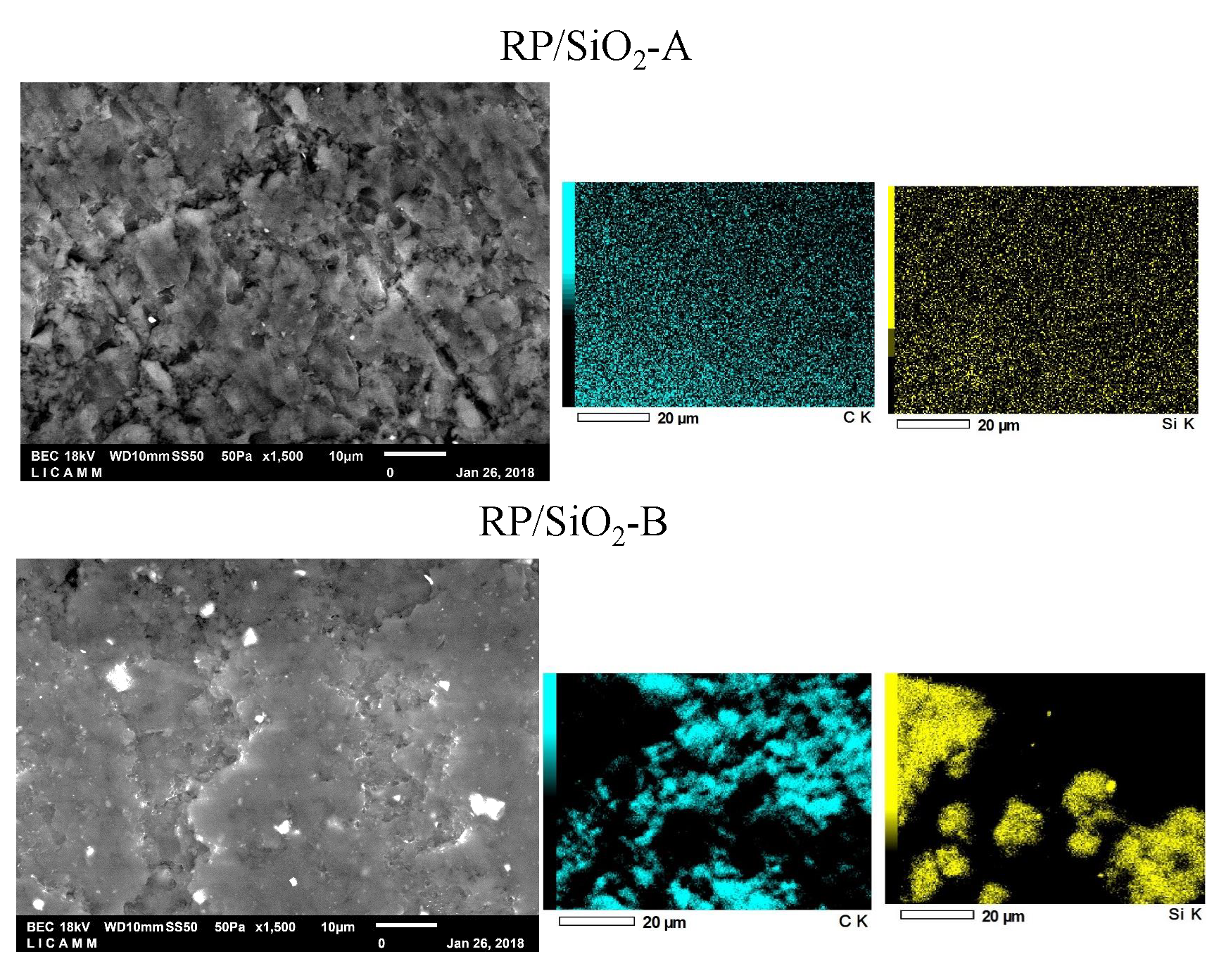 |
|
Compound materials obtained by polyester resin reinforced with silica nanoparticles (RP/SiO2) were characterized by different mechanical essays. Test tubes were obtained under ASTM norms with SiO2 concentrations around 0.5 to 5% of weight. Compression tests indicated that silica nanoparticles lead to formation of ductile materials with respect to the polymer resin; compression deformation percentages (%e) were determined around 45-52 %; also, while the material resistance reached 90MPa. These materials showed a 38-67% increase in the bending module, and an increase of 16 to 34% in the absorption of impact energy. After mechanical characterization, was carried out a simulation of the mechanical behavior of bumper fascia made with the RP/SiO2-A using finite element software. Frontal and lateral collision indicated a maximum stress around 21.5 MPa and 28.36 MPa respectively, these results suggested that the auto-part will only show plastic deformation in some areas; due to the elastic limit for RP/SiO2 is 26 MPa and its maximum resistance at 89.8 MPa
Keywords: Composite materials; SiO2 nanoparticles; mechanical properties; simulation mechanical behavior.
|
|
 |

