 |
|
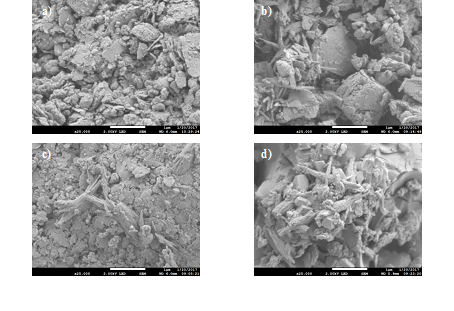
In the present work, the changes in the natural dolomite produced by calcination with CO2 laser was analyzed, the power density and irradiation time of the CO2 laser were varied. The characterization of each sample in terms of changes produced by radiation was obtained. For this, a mineral analysis was carried out by Scanning Electron Microscopy (SEM), Energy Dispersive Spectroscopy (EDS) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD). The EDS analysis revealed the presence of elements such as Mg, Si, Al, Ca, O, Fe, Z and Na, while the X-ray diffraction analysis suggested that the treated dolomite samples experienced slight changes in their crystalline structure when they were calcined with the CO2 laser, however, there were no changes in the main phase of the dolomite but there was a decrease in the intensities of the signals. Additionally, a photocatalytic study was performed on the degradation of the Azo dye Reactive Black 5 (RB5) in an acid aqueous medium using natural dolomite and natural dolomite calcined with the CO2 laser. UV / VIS spectrophotometry was used for the characterization of the photocatalytic tests. An increase in the degradation and decolorization speed of the Black 5 dye was observed.
Keywords: laser, dolomite, black 5, photocatalysis, laser radiation.
|
|
 |

