 |
|
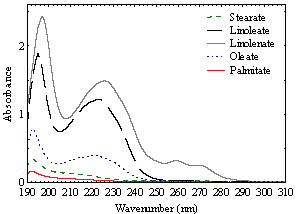
Biodiesel is an alternative fuel and can be obtained by the transesterification of vegetable oils. Spectrophotometric methods can be used for the quantification of mixtures, associated with chemometric tools, enabling the analysis of overlapping signals. The aim of this work is to apply the multivariate calibration with PLS (partial least squares) and artificial neural network (ANN), to estimate the concentration of esters in the transesterification of soybean oil using molecular absorption spectrophotometry as analytical technique. Absorbance measurements were performed in a spectrophotometer UV/VIS. Synthetic solutions were prepared with standards of the five major compounds of soybean biodiesel and real samples were obtained by the reaction of transesterification of soybean oil with NaOH and enzymatic method was used Lipozyme® IM (Novozymes), as catalysts. Results shows that all components of this reaction medium absorb in the wavelength range of 190-280 nm. Reactions of basic catalysis reached conversions close to 100%, while enzymatic reactions reached lower conversions. For both methods, calibration and validation groups were composed, respectively, by synthetic and real samples. Results showed that the concentrations of esters estimated by ANN model in the real samples are more accurate (R2-0.93), showing the good ability to estimation of ANN.
Keywords: biofuels, chromatography, enzymology, spectroscopy.
|
|
 |

