 |
|
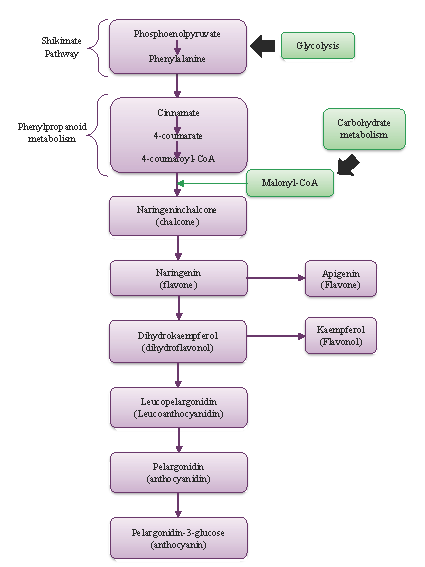
In the last years, the interest and use of bioactive phenolic compounds has increased in food and pharmaceutical fields, this mainly because of the benefits reported by many researchers i.e. antioxidant activity and their potential use as nutraceuticals. Unfortunately, all these benefits are linked generally with their stability, which may be weak depending on the environment conditions. In this tenor, microencapsulation could be a technological option to preserve those molecules and provide them the desired stability. Furthermore, it may permit a better managing and masking of the astringent taste that most of phenolic compounds have. In this review encapsulation techniques such as spray drying, extrusion, molecular inclusion in cyclodextrins, electrospray and liposomes are discussed, also the different wall materials, including polysaccharides, proteins, whey protein, different mucilages, inulin, zein and FucoPol are described.
Keywords: antioxidants, nutraceuticals, polyphenols, microencapsulation, wall material.
|
|
 |

