Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 19, No. 2 (2020), IA637
Treatment of wastewater from the petrochemical industry by a chemical Fenton process
|
R. Contreras-Bustos, J. Cardenas-Mijangos, A. Dector-Espinoza, A. Rodriguez-García, L. Montoya-Herrera, J. Jiménez-Becerril
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/IA637
Abstract
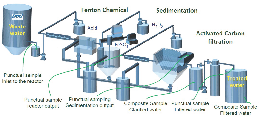 |
|
Advanced oxidation processes aid in the degradation of contaminating organic matter, as they can form easily degradable compounds by biologic processes or break organic matter down to its minerals. In this study, it was tested the Fenton process of chemical oxidation for organic matter degradation of petrochemical wastewater with chemical oxygen demand (COD) higher than 20 g/L. In batch testing, it was used the statistical factorial experiments design, confirmed by verification tests utilizing various concentrations in water and subsequently in continuous flow in a pilot plant by oxidation under the Fenton process. Variables’ effects on contaminant degradation in water follow an order: pH > relation Fe2+/H2O2 > time > [H2O2]. The Fenton process removes more than 50% of contaminants in COD testing and more than 70% in continuous testing. Easily oxidated organic matter consumes H2O2 at the beginning of the process, whereas organic matter that was more difficult to degrade was oxidized with a hydroxyl radical (OH•).
Keywords: Wastewater; Petrochemical industry; Fenton process; Pilot test.
|
|
 |

