 |
|
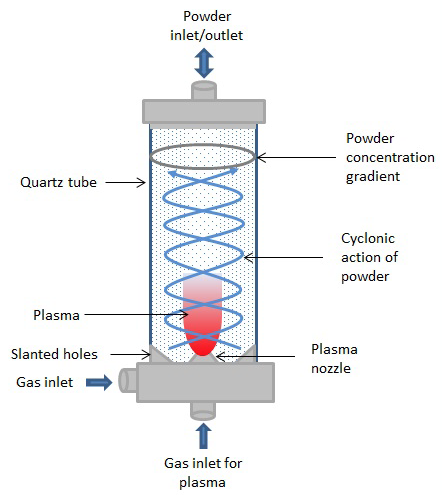
A swirling fluidized bed reactor design for the preparation of supported nanoparticles is reported. It uses a DC plasma torch that decomposes and vaporizes salt precursors; the cationic part condenses as metal nanoparticles on a powder support. Any fluidizable granular material can be used as support, as long as it withstands the temperatures of the plasma torch. The torch is located at the center of the reactor axis and the powder is fluidized using a cyclonic action (swirl) to minimize the space where the grains could come into direct contact with the plasma zone. The reactor was tested for silver nanoparticles (AgNPs) supported on silica-alumina, using silver nitrate as precursor. The results show large grains decorated with nano-sized metal particles. Depending on the load of silver nitrate, the size of the nanoparticles can range from 3 to 50 nm, as measured using transmission electron microscopy. They are in a non-oxidized state, as revealed with x-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The AgNPs/SiO2–Al2O3 composite was tested as a catalyst in the hydrodesulphurization of dibenzothiophene. This method can be scaled up to produce large quantities of supported metallic particles. Its inherent simplicity, high processing speed and the low operating cost are its main advantages.
Keywords: silver nanoparticles, fluidized bed, swirling bed, plasma reactor, hydrodesulphurization.
|
|
 |

