 |
|
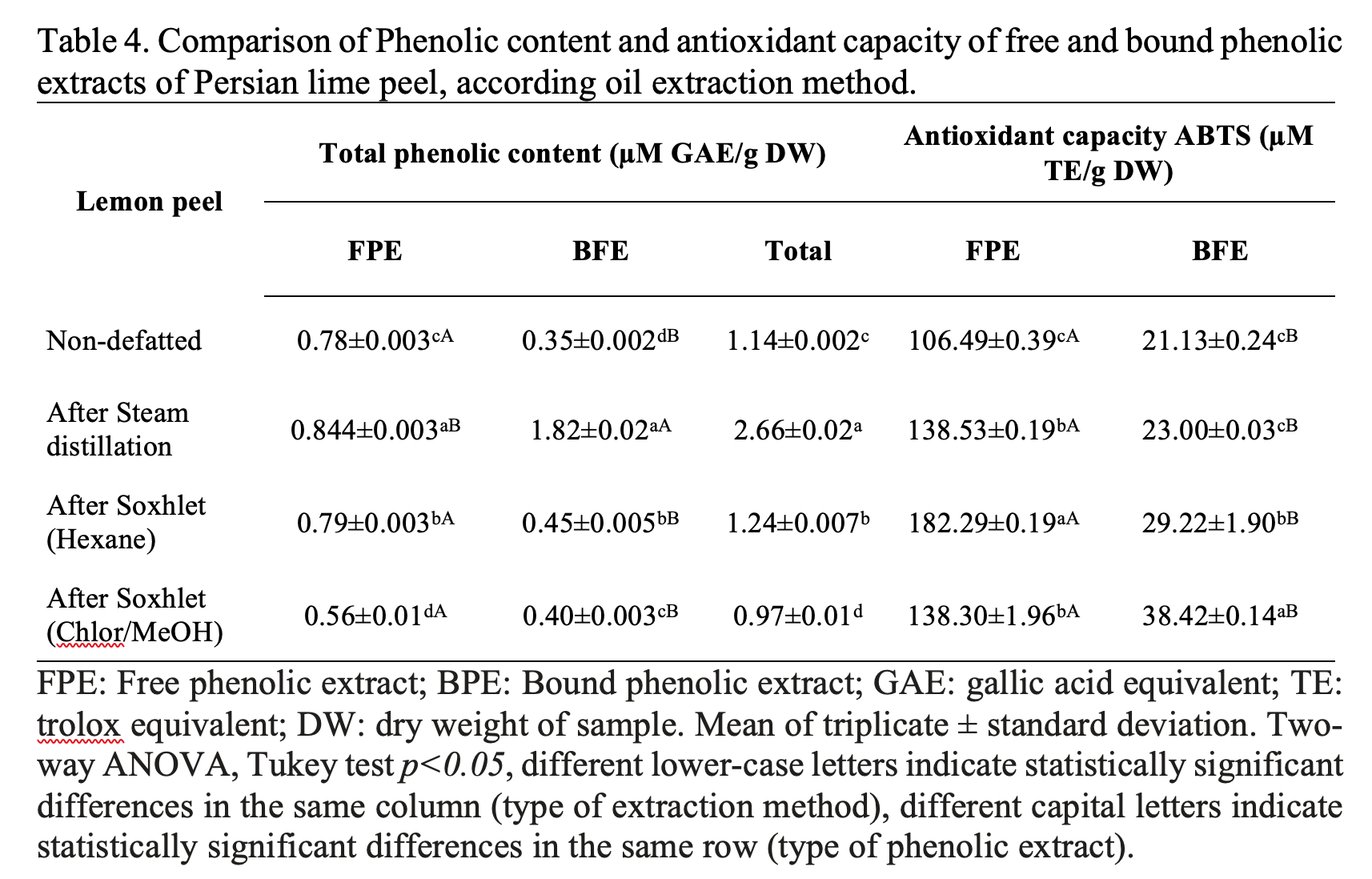
Mexico's Persian lime production in 2019 was close to 1.3 million of tons, inferring an approximately 390,000 tons of peel residues during its processing. This residues presents an interesting opportunity for obtaining value-added products, mainly due to its composition, formed principally by water, soluble sugars, fiber, organic acids, fatty acids, minerals, essential oils, flavonoids, and vitamins. Despite this, the valorisation of this residual biomass has been almost completely ignored. In this paper, the residual peel was analyzed in order to determine its biotechnological potential, for this, different oil extraction methods were compared, the fatty acids profile was determined, also characterization and the antioxidant potential of the defatted residues were evaluated. The results showed that the principal fatty acids present in the oil extracted were Palmitic, Oleic and Linoleic, which allows its use for food and bioenergy purposes, moreover, the defatted residual biomass characterization presents a chemical composition which allows the use for as livestock, biogas production or agronomy. To our knowledge, this is the first report of antioxidant activity from defatted Persian lime residual biomass, wherein, the residues generated by steam distillation showed the bigger amount of phenolic compounds, but the obtained from hexane extraction presents a higher antioxidant activity.
Keywords: persian lime, oil extraction, valorisation, phenolic compounds, antioxidant activity.
|
|
 |

