 |
|
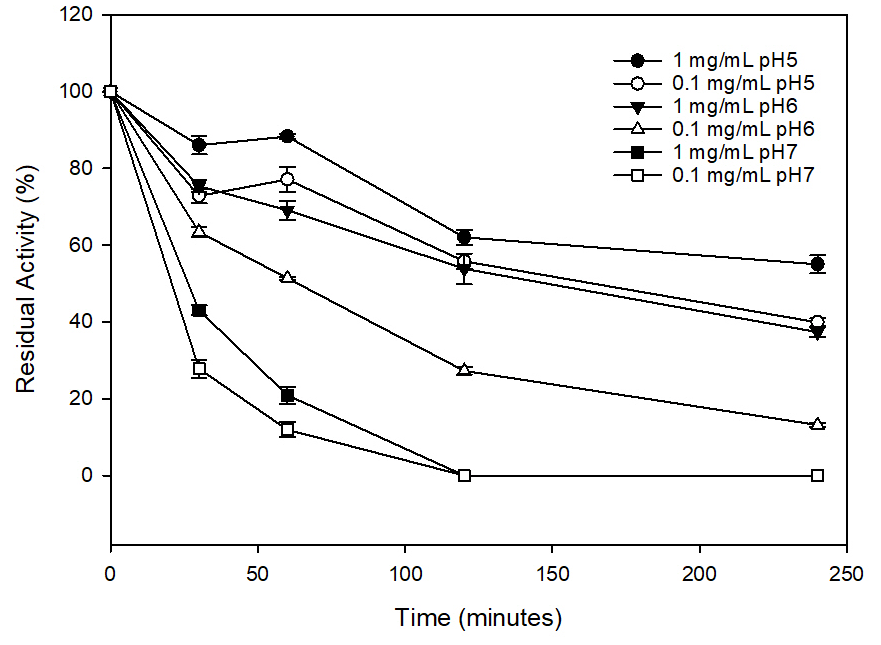
The β-glucosidase from almond was immobilized using different strategies: ionic adsorption on aminated MANAE-agarose beads at pH 5, 7 and 9, followed by glutaraldehyde pre-activated supports. The pH of the immobilization was altered to allow different enzyme molecule orientations on the support surface. The concentration of the enzyme exhibited an effect on the stability of the free enzyme. Immobilization by ion exchange maintained up to 80\% of the activity of β-glucosidase, however the stabilization was lower than the immobilization by covalent binding on pre-activated supports. The enzyme immobilized on supports pre-activated at pH 5 showed a higher activity of 78\% after 24 h. The immobilized enzymes were inactivated at pH 5 and 7, the enzyme immobilized at pH 7 and inactivated at pH 5 maintained greater stability than the immobilized at the other pH values. Considering the enzymatic activity, the stability and the kinetic parameters Km, Vmax and the Km/Ki ratio, the β-glucosidase immobilized on supports pre-activated with glutaraldehyde at pH 5 and 7 are the best option to use β-glucosidase from almonds.
Keywords: β-glucosidase, enzyme immobilization, glutaraldehyde, amino-agarose supports, enzyme stabilization.
|
|
 |

