Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 21, No. 2 (2022), IA2680
Anaerobic digestion of agro-industrial waste: Anaerobic lagoons in Latin America
|
U. Galván-Arzola, L.R. Miramontes-Martínez, C. Escamilla-Alvarado, J.E. Botello-Álvarez, M.M. Alcalá-Rodríguez, R. Valencia-Vázquez, P. Rivas-García
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/IA2680
Abstract
 |
|
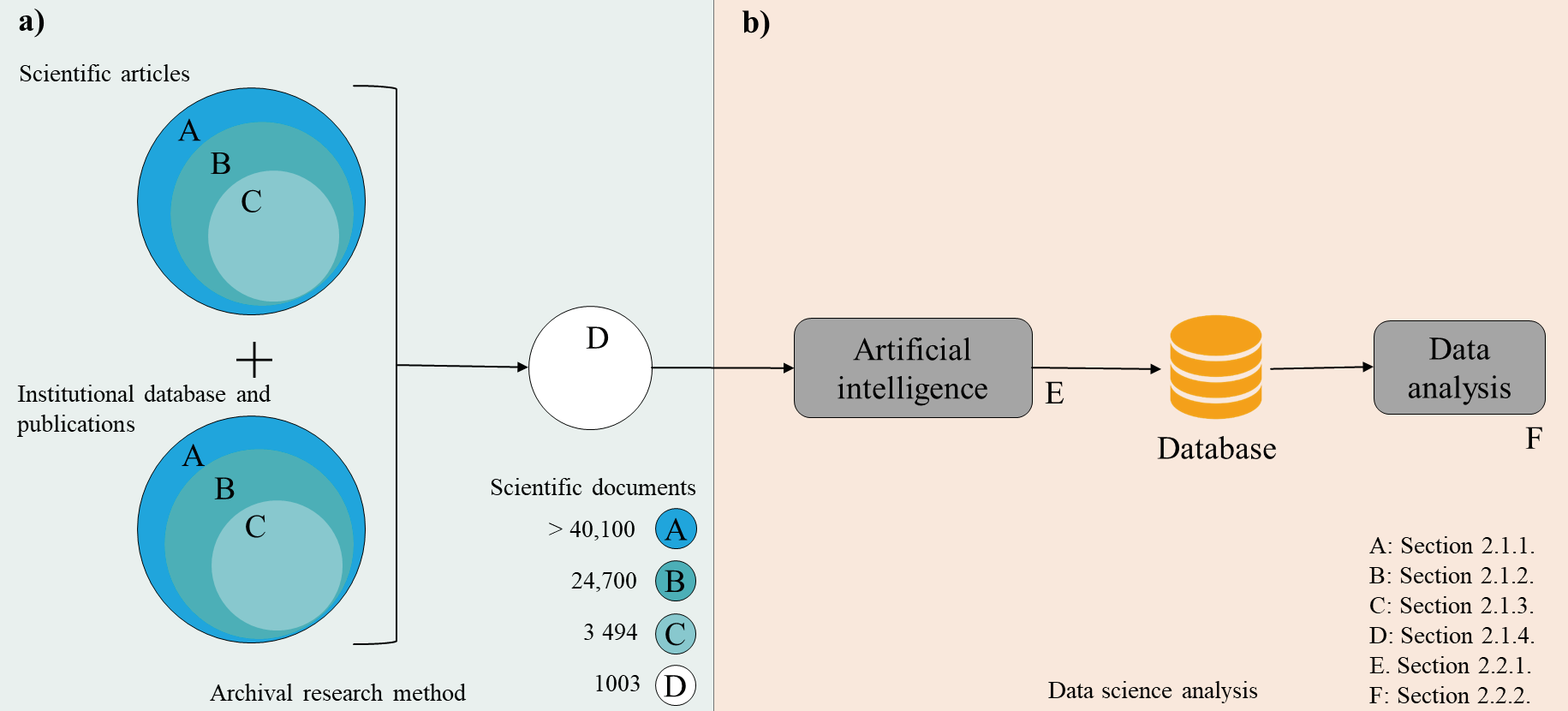
In developed countries, the valorization of agro-industrial wastes (AW) using waste-to-energy strategies through anaerobic digestion (AD) is a reality. In Latin America (LATAM), there are different problems in the management of AW from intensive livestock farming. This study aims to provide a pseudo-radiography of AD management systems focusing on covered anaerobic lagoons (CALs) in Latin America. Quantitative and qualitative data from 1,003 scientific papers were synthesized and analyzed to form a database using data science, which allowed evaluation of the congruence of the scientific research with the real problems of LATAM management. Thirty-eight types of inhibition phenomena with 5,264 mentions were addressed in the database. Nitrogen-related AD inhibition phenomena represented 21% of the incidences in this study, besides being the most significant phenomenon in covered anaerobic lagoons in LATAM. The results showed that CALs in the region are the principal AW management systems (mainly bovine and swine manure) and that scientific research in this sector does not address the real problems in the sector.
Keywords: Anaerobic lagoons; anaerobic digestion; data science; agro-industrial wastes; inhibition phenomena.
|
|
 |

