Revista Mexicana de Ingeniería Química, Vol. 22, No. 1 (2023), Bio3025
Respiro-fermentative metabolism in yeast cultivated in solid-state culture: The Crabtree effect and ethanol production
|
R.J. Estrada-Martínez, E. Favela-Torres, N. O. Soto-Cruz, G. Saucedo-Castañeda, F. J. Martínez-Valdez
https://doi.org/10.24275/rmiq/Bio3025
Abstract
 |
|
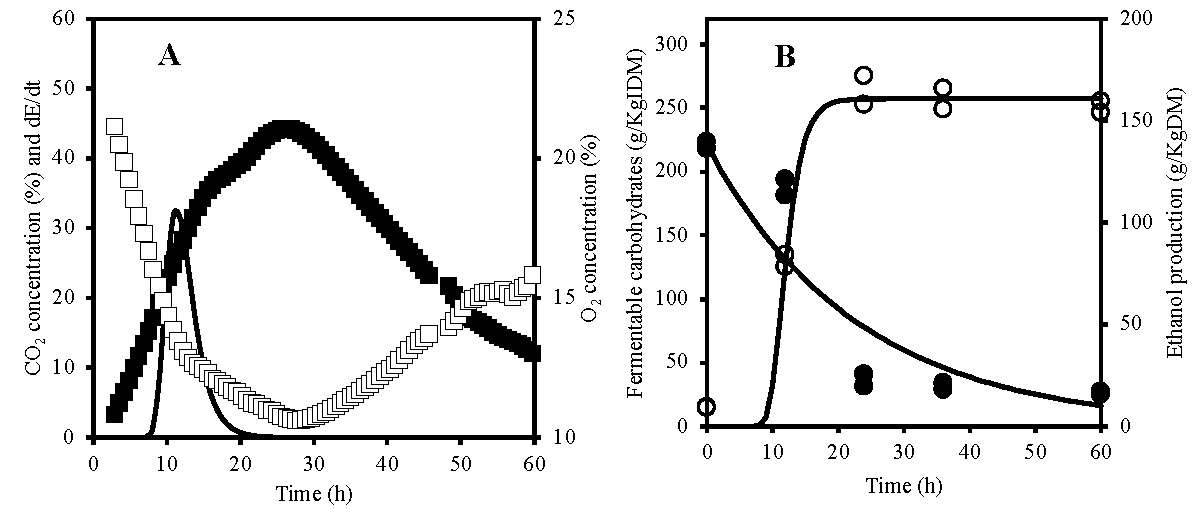
A strong inoculum in solid-state culture (SSC) is achieved by using a high-density, high-activity microbial population. To determine the best conditions for yeast propagation, the Crabtree effect was analyzed. Inoculum production was carried out in Erlenmeyer flasks with different designs (baffled, coiled and conventional) and filling volumes (20 and 40 %). A 20% filling volume resulted in better air diffusion, leading to improved yeast growth independently of the flask configuration. Yeasts have adapted to produce ethanol under aerobic conditions to compete with other microorganisms. With commercial baker's yeast, the highest ethanol production was achieved at the laboratory scale (195.70 ±17.25 g ethanol/kg dry matter [DM]). There was no difference in ethanol production between the tubular reactor (171.10 ± 10.87 g ethanol/kg DM) and in the pilot batch bioreactor (165.03 ± 9.90 g ethanol/kg DM) using S. cerevisiae yeast ITD00196 as inoculum. Crabtree-positive yeasts have potential for rapid ethanol production in organic waste fermentation without thermochemical or enzymatic pre-treatment by SSC in the laboratory and at pilot-scale.
Keywords: Respiro-fermentative metabolism; Crabtree effect; solid-state culture; ethanol production.
|
|
 |

