 |
|
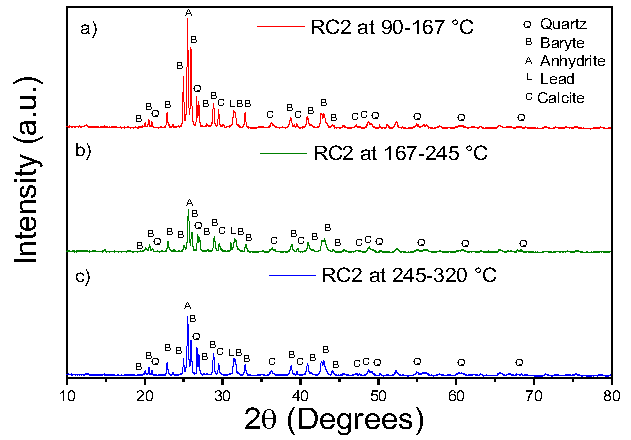
In Mexico's hydrocarbon sector, drilling waste represents a problem because the techniques to treat it increase production costs. In this regard, thermal desorption represents a good option, even though it presents variations in hydrocarbon removals, which causes added costs since some residues need to be treated again. Thus, the objective of this study was to identify these variations according to the treatment temperature (< 320 ° C) on a laboratory scale. The results showed that the samples had minerals in common (quartz, baryte and anhydrite) that did not vary after the treatments. However, other minerals were found in some samples, which were not present in others. The hydrocarbons decreased with respect to the temperature fluctuations. However, when comparing the removed percentages and the fractions, they were different from each other. Moreover, Cd, Cr, Pb, Ni, Zn, V, Ba, Fe, and Mn were detected, but their concentration in the leachates was low. It was concluded that the variation in the constituents of the drilling cuttings could depend on the source of generation and that this factor could influence the final properties of the treated solid. When the removal of hydrocarbons was achieved, the fractions there, and the concentration of metals were different between the samples.
Keywords: Metal, Hydrocarbon, Mineralogy, Waste.
|
|
 |

