 |
|
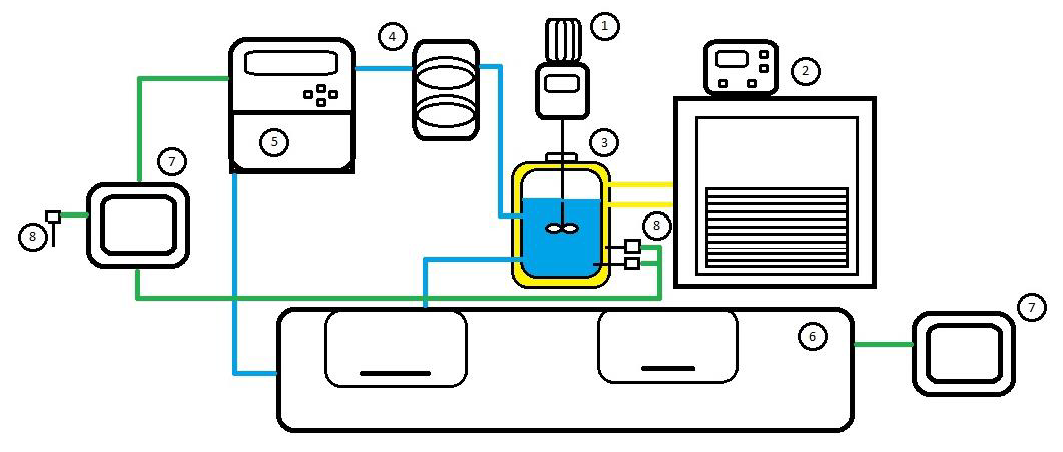
In this work, the interfacial energy of the acetylsalicylic acid-ethanol system was evaluated using experimental results of the metastable zone width (MSZW) obtained at the following operation conditions: agitation rate (230 and 400 rpm), cooing rate (6, 9 12 and 15 K/h) and saturation temperature (288.15, 293.15, 298.15, 303.15, 308.15 and 313.15 K). A nonlinear regression algorithm and an easy to implement a lineal integration algorithm of the number density of nuclei were used to determine the interfacial energy. The results obtained with the two integral strategies were compared with the values obtained with the 3D nucleation theory. Interfacial energies obtained with the nonlinear regression presented a difference smaller than 6.5 % but estimations determined with the lineal integration algorithm had an average difference of 48.6 %.
Keywords: acetylsalicylic acid, anhydrous ethanol, crystallization, integral method, interfacial energy.
|
|
 |

